Update README.md
Browse files
README.md
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
dataset_info:
|
| 3 |
features:
|
| 4 |
- name: id
|
|
@@ -38,4 +39,83 @@ configs:
|
|
| 38 |
path: data/test-*
|
| 39 |
- split: validation
|
| 40 |
path: data/validation-*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 41 |
---
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
---
|
| 2 |
+
license: mit
|
| 3 |
dataset_info:
|
| 4 |
features:
|
| 5 |
- name: id
|
|
|
|
| 39 |
path: data/test-*
|
| 40 |
- split: validation
|
| 41 |
path: data/validation-*
|
| 42 |
+
task_categories:
|
| 43 |
+
- text-generation
|
| 44 |
+
language:
|
| 45 |
+
- en
|
| 46 |
+
tags:
|
| 47 |
+
- unit test
|
| 48 |
+
- java
|
| 49 |
+
- code
|
| 50 |
---
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
## Dataset Description
|
| 53 |
+
Microsoft created the methods2test dataset, consisting of Java Junit test cases with its corresponding focal methods.
|
| 54 |
+
It contains 780k pairs of JUnit test cases and focal methods which were extracted from a total of 91K
|
| 55 |
+
Java open source project hosted on GitHub.
|
| 56 |
+
|
| 57 |
+
This is smaller subset of the assembled version of the methods2test dataset.
|
| 58 |
+
It provides convenient access to the different context levels based on the raw source code (e.g. newlines are preserved). The test cases and associated classes are also made available.
|
| 59 |
+
The subset is created by taking only one sample from each of the 91k projects.
|
| 60 |
+
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
The mapping between test case and focal methods are based heuristics rules and Java developer's best practice.
|
| 63 |
+
|
| 64 |
+
More information could be found here:
|
| 65 |
+
- [methods2test Github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/methods2test)
|
| 66 |
+
- [Methods2Test: A dataset of focal methods mapped to test cases](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.12776.pdf)
|
| 67 |
+
|
| 68 |
+
## Dataset Schema
|
| 69 |
+
```
|
| 70 |
+
t: <TEST_CASE>
|
| 71 |
+
t_tc: <TEST_CASE> <TEST_CLASS_NAME>
|
| 72 |
+
fm: <FOCAL_METHOD>
|
| 73 |
+
fm_fc: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD>
|
| 74 |
+
fm_fc_c: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS>
|
| 75 |
+
fm_fc_c_m: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS> <METHOD_SIGNATURES>
|
| 76 |
+
fm_fc_c_m_f: <FOCAL_CLASS_NAME> <FOCAL_METHOD> <CONTRSUCTORS> <METHOD_SIGNATURES> <FIELDS>
|
| 77 |
+
```
|
| 78 |
+
|
| 79 |
+
## Focal Context
|
| 80 |
+
- fm: this representation incorporates exclusively the source
|
| 81 |
+
code of the focal method. Intuitively, this contains the most
|
| 82 |
+
important information for generating accurate test cases for
|
| 83 |
+
the given method.
|
| 84 |
+
- fm+fc: this representations adds the focal class name, which
|
| 85 |
+
can provide meaningful semantic information to the model.
|
| 86 |
+
- fm+fc+c: this representation adds the signatures of the constructor methods of the focal class. The idea behind this
|
| 87 |
+
augmentation is that the test case may require instantiating
|
| 88 |
+
an object of the focal class in order to properly test the focal
|
| 89 |
+
method.
|
| 90 |
+
- fm+fc+c+m: this representation adds the signatures of the
|
| 91 |
+
other public methods in the focal class. The rationale which
|
| 92 |
+
motivated this inclusion is that the test case may need to
|
| 93 |
+
invoke other auxiliary methods within the class (e.g., getters,
|
| 94 |
+
setters) to set up or tear down the testing environment.
|
| 95 |
+
- fm+fc+c+m+f : this representation adds the public fields of
|
| 96 |
+
the focal class. The motivation is that test cases may need to
|
| 97 |
+
inspect the status of the public fields to properly test a focal
|
| 98 |
+
method.
|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
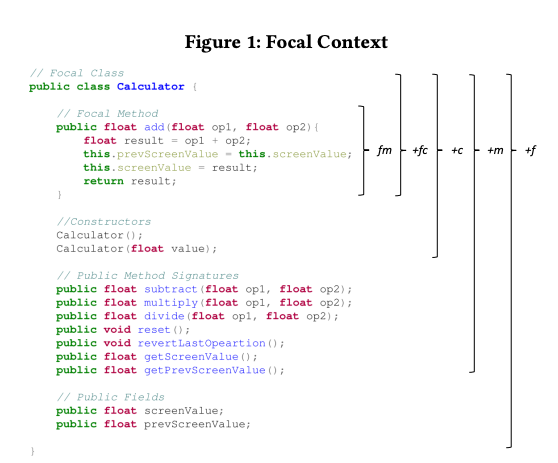
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
The different levels of focal contexts are the following:
|
| 103 |
+
```
|
| 104 |
+
T: test case
|
| 105 |
+
T_TC: test case + test class name
|
| 106 |
+
FM: focal method
|
| 107 |
+
FM_FC: focal method + focal class name
|
| 108 |
+
FM_FC_C: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures
|
| 109 |
+
FM_FC_C_M: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures + public method signatures
|
| 110 |
+
FM_FC_C_M_F: focal method + focal class name + constructor signatures + public method signatures + public fields
|
| 111 |
+
```
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+
## Limitations
|
| 114 |
+
The original authors validate the heuristics by inspecting a
|
| 115 |
+
statistically significant sample (confidence level of 95% within 10%
|
| 116 |
+
margin of error) of 97 samples from the training set. Two authors
|
| 117 |
+
independently evaluated the sample, then met to discuss the disagreements. We found that 90.72% of the samples have a correct
|
| 118 |
+
link between the test case and the corresponding focal method
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
## Contribution
|
| 121 |
+
All thanks to the original authors.
|