Spaces:
Sleeping
Sleeping
Commit
·
87360eb
1
Parent(s):
93fea1b
Debug: parsing detections
Browse files
app.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -1,40 +1,55 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
import numpy as np
|
| 2 |
-
import
|
| 3 |
-
|
| 4 |
-
|
| 5 |
-
|
| 6 |
-
|
| 7 |
-
|
| 8 |
-
|
| 9 |
-
|
| 10 |
-
|
| 11 |
-
|
| 12 |
-
|
| 13 |
-
|
| 14 |
-
|
| 15 |
-
|
| 16 |
-
|
| 17 |
-
|
| 18 |
-
|
| 19 |
-
|
| 20 |
-
|
| 21 |
-
|
| 22 |
-
|
| 23 |
-
|
| 24 |
-
|
| 25 |
-
|
| 26 |
-
|
| 27 |
-
|
| 28 |
-
|
| 29 |
-
|
| 30 |
-
|
| 31 |
-
|
| 32 |
-
|
| 33 |
-
|
| 34 |
-
|
| 35 |
-
|
| 36 |
-
|
| 37 |
-
|
| 38 |
-
|
| 39 |
-
|
| 40 |
-
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import torch
|
| 2 |
+
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForMaskedLM
|
| 3 |
+
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
| 4 |
import numpy as np
|
| 5 |
+
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
|
| 6 |
+
|
| 7 |
+
# Load a pre-trained model and tokenizer
|
| 8 |
+
model_name = 'bert-base-uncased'
|
| 9 |
+
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 10 |
+
model = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
# Example input text
|
| 13 |
+
text = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
|
| 14 |
+
|
| 15 |
+
# Tokenize the input text
|
| 16 |
+
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 17 |
+
input_ids = inputs['input_ids']
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
# Get attention weights by running the model
|
| 20 |
+
with torch.no_grad():
|
| 21 |
+
outputs = model(input_ids, output_attentions=True)
|
| 22 |
+
|
| 23 |
+
# Extract the attention weights (size: [num_layers, num_heads, seq_len, seq_len])
|
| 24 |
+
attention_weights = outputs.attentions
|
| 25 |
+
|
| 26 |
+
# Select a specific layer and attention head
|
| 27 |
+
layer_idx = 0 # First layer
|
| 28 |
+
head_idx = 0 # First attention head
|
| 29 |
+
|
| 30 |
+
# Get the attention matrix for this layer and head
|
| 31 |
+
attention_matrix = attention_weights[layer_idx][0][head_idx].cpu().numpy()
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
# Use t-SNE to reduce the dimensionality of the attention matrix (embedding space)
|
| 34 |
+
# Attention matrix shape: [seq_len, seq_len], so we reduce each row (which corresponds to a token's attention distribution)
|
| 35 |
+
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2, random_state=42)
|
| 36 |
+
reduced_attention = tsne.fit_transform(attention_matrix)
|
| 37 |
+
|
| 38 |
+
# Plotting the reduced attention embeddings
|
| 39 |
+
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
|
| 40 |
+
|
| 41 |
+
# Plot the reduced attention in 2D
|
| 42 |
+
ax.scatter(reduced_attention[:, 0], reduced_attention[:, 1])
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
# Annotate the tokens in the scatter plot
|
| 45 |
+
tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[0])
|
| 46 |
+
for i, token in enumerate(tokens):
|
| 47 |
+
ax.annotate(token, (reduced_attention[i, 0], reduced_attention[i, 1]), fontsize=12, ha='right')
|
| 48 |
+
|
| 49 |
+
# Display the plot
|
| 50 |
+
plt.title(f"t-SNE Visualization of Attention - Layer {layer_idx+1}, Head {head_idx+1}")
|
| 51 |
+
plt.xlabel("t-SNE Dimension 1")
|
| 52 |
+
plt.ylabel("t-SNE Dimension 2")
|
| 53 |
+
plt.grid(True)
|
| 54 |
+
plt.show()
|
| 55 |
+
plt.savefig('test.png')
|
test.png
ADDED
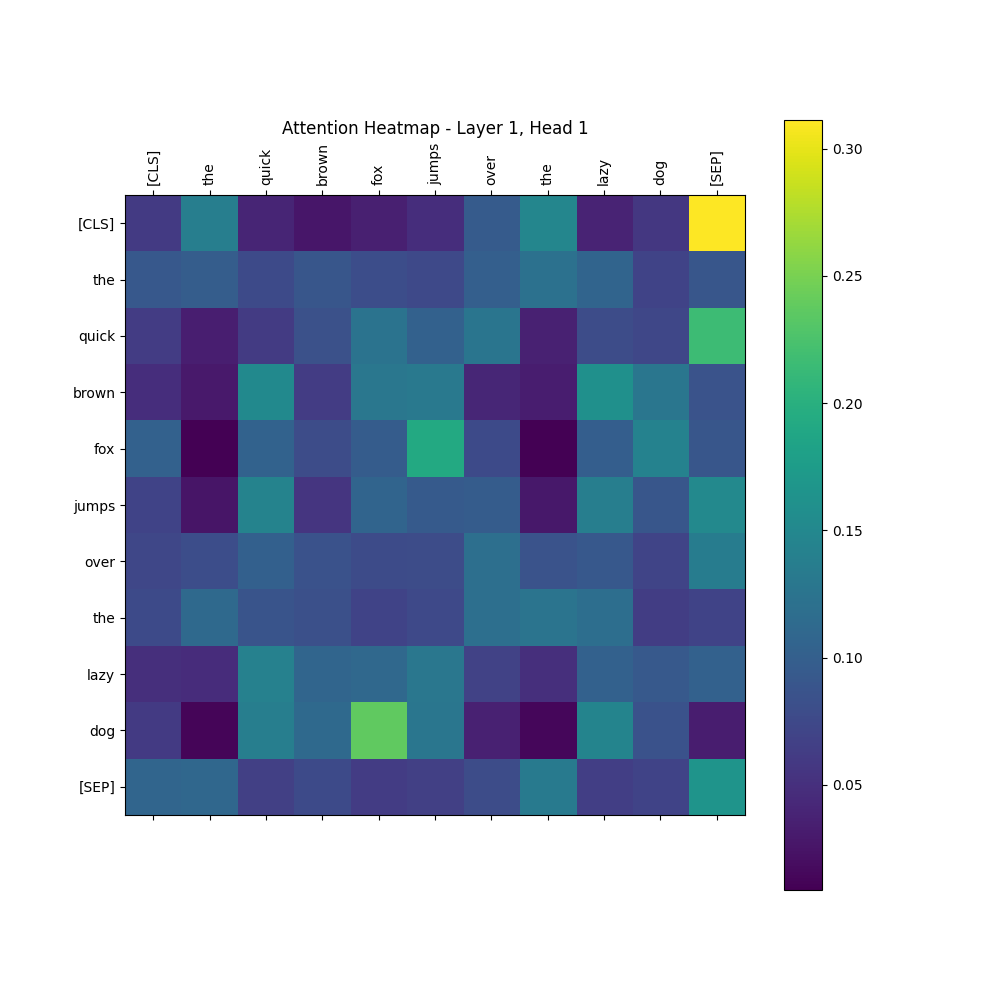
|
test.py
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
import torch
|
| 2 |
+
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForMaskedLM
|
| 3 |
+
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
| 4 |
+
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
|
| 5 |
+
import numpy as np
|
| 6 |
+
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
# Load a pre-trained model and tokenizer
|
| 9 |
+
model_name = 'bert-base-uncased'
|
| 10 |
+
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 11 |
+
model = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
| 12 |
+
|
| 13 |
+
# Example input text
|
| 14 |
+
text = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
# Tokenize the input text
|
| 17 |
+
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
| 18 |
+
input_ids = inputs['input_ids']
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
# Get attention weights by running the model
|
| 21 |
+
with torch.no_grad():
|
| 22 |
+
outputs = model(input_ids, output_attentions=True)
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
# Extract the attention weights (size: [num_layers, num_heads, seq_len, seq_len])
|
| 25 |
+
attention_weights = outputs.attentions
|
| 26 |
+
|
| 27 |
+
# Select a specific layer and attention head
|
| 28 |
+
layer_idx = 0 # First layer
|
| 29 |
+
head_idx = 0 # First attention head
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
# Get the attention matrix for this layer and head
|
| 32 |
+
attention_matrix = attention_weights[layer_idx][0][head_idx].cpu().numpy()
|
| 33 |
+
|
| 34 |
+
# Use t-SNE to reduce the dimensionality of the attention matrix (embedding space)
|
| 35 |
+
# Attention matrix shape: [seq_len, seq_len], so we reduce each row (which corresponds to a token's attention distribution)
|
| 36 |
+
tsne = TSNE(n_components=3, random_state=42, perplexity=5) # Set a lower perplexity value
|
| 37 |
+
reduced_attention = tsne.fit_transform(attention_matrix)
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
# Plotting the reduced attention embeddings in 3D
|
| 40 |
+
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
|
| 41 |
+
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
|
| 42 |
+
|
| 43 |
+
# Plot the reduced attention in 3D
|
| 44 |
+
ax.scatter(reduced_attention[:, 0], reduced_attention[:, 1], reduced_attention[:, 2])
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
# Annotate the tokens in the scatter plot
|
| 47 |
+
tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input_ids[0])
|
| 48 |
+
for i, token in enumerate(tokens):
|
| 49 |
+
ax.text(reduced_attention[i, 0], reduced_attention[i, 1], reduced_attention[i, 2],
|
| 50 |
+
token, fontsize=12, ha='center')
|
| 51 |
+
|
| 52 |
+
# Set plot labels
|
| 53 |
+
ax.set_title(f"3D t-SNE Visualization of Attention - Layer {layer_idx+1}, Head {head_idx+1}")
|
| 54 |
+
ax.set_xlabel("t-SNE Dimension 1")
|
| 55 |
+
ax.set_ylabel("t-SNE Dimension 2")
|
| 56 |
+
ax.set_zlabel("t-SNE Dimension 3")
|
| 57 |
+
|
| 58 |
+
plt.show()
|
yolov8.py
CHANGED
|
@@ -56,19 +56,34 @@ def xai_yolov8n(image):
|
|
| 56 |
# Check if GPU is available and use it
|
| 57 |
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
|
| 58 |
model.to(device)
|
|
|
|
| 59 |
target_layers = [model.model.model[-2]] # Grad-CAM target layer
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 60 |
results = model([image])
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 61 |
if isinstance(results, list):
|
| 62 |
results = results[0] # Extracting the first result (if list)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 63 |
|
|
|
|
| 64 |
boxes, colors, names = parse_detections([results]) # Ensure results are passed as a list
|
| 65 |
detections_img = draw_detections(boxes, colors, names, image.copy())
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 66 |
img_float = np.float32(image) / 255
|
| 67 |
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
|
| 68 |
tensor = transform(img_float).unsqueeze(0).to(device) # Ensure tensor is on the right device
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 69 |
cam_image, renormalized_cam_image = generate_cam_image(model, target_layers, tensor, image, boxes)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 70 |
final_image = np.hstack((image, cam_image, renormalized_cam_image))
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
# Return final image and a caption
|
| 73 |
caption = "Results using YOLOv8n"
|
| 74 |
-
return Image.fromarray(final_image), caption
|
|
|
|
| 56 |
# Check if GPU is available and use it
|
| 57 |
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
|
| 58 |
model.to(device)
|
| 59 |
+
|
| 60 |
target_layers = [model.model.model[-2]] # Grad-CAM target layer
|
| 61 |
+
|
| 62 |
+
# Process the image through the model
|
| 63 |
results = model([image])
|
| 64 |
+
|
| 65 |
+
# If results are a list, extract the first element (detected results)
|
| 66 |
if isinstance(results, list):
|
| 67 |
results = results[0] # Extracting the first result (if list)
|
| 68 |
+
|
| 69 |
+
# Ensure that outputs are in tensor form
|
| 70 |
+
logits = results.pred[0] # Get the prediction tensor from the results
|
| 71 |
|
| 72 |
+
# Parse the detections
|
| 73 |
boxes, colors, names = parse_detections([results]) # Ensure results are passed as a list
|
| 74 |
detections_img = draw_detections(boxes, colors, names, image.copy())
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
# Prepare image for Grad-CAM
|
| 77 |
img_float = np.float32(image) / 255
|
| 78 |
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
|
| 79 |
tensor = transform(img_float).unsqueeze(0).to(device) # Ensure tensor is on the right device
|
| 80 |
+
|
| 81 |
+
# Generate CAM images
|
| 82 |
cam_image, renormalized_cam_image = generate_cam_image(model, target_layers, tensor, image, boxes)
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+
# Combine original image, CAM image, and renormalized CAM image
|
| 85 |
final_image = np.hstack((image, cam_image, renormalized_cam_image))
|
| 86 |
|
| 87 |
# Return final image and a caption
|
| 88 |
caption = "Results using YOLOv8n"
|
| 89 |
+
return Image.fromarray(final_image), caption
|