Argonne-1.0 🌌
Argonne-1.0 is a language model pretrained from scratch on the Fineweb-Edu dataset, specifically designed for research, educational purposes, and exploration into language modeling.
📚 Dataset
The model is pretrained on Fineweb-Edu (CC-MAIN-2024-10), an open and comprehensive dataset consisting of educational web content.
🚀 Model Architecture
Argonne-1.0 is a GPT-like autoregressive transformer model with approximately 276M parameters:
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
n_layer |
12 |
n_head |
12 |
n_embd |
1296 |
block_size |
2048 |
dropout |
0.1 |
| Parameters | 275,827,680 |
🔗 GitHub Repository
The training and inference scripts for Argonne-1.0 are hosted on GitHub:
👉 https://github.com/PursuitOfDataScience/ArgonneAI
🛠️ Training Details
Training was conducted on a single NVIDIA DGX node:
- Hardware: 8× NVIDIA A100 GPUs (80GB HBM each)
- Training duration: 1440 GPU hours (~180 hours wall-clock on 8 GPUs)
- Total steps: 160,000 global steps
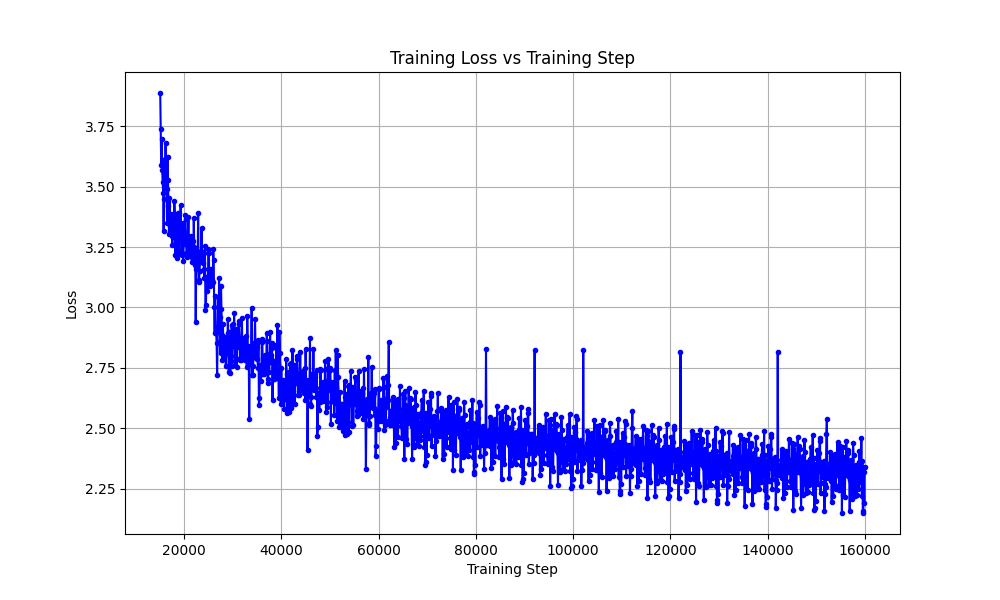
📈 Training Loss Curve
Here's the training loss progression:
Inference
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
snapshot_download(repo_id="PursuitOfDataScience/Argonne-1.0")
You can run the following sample code to use the model for text generation:
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Register the model architecture with AutoModel
from mp_pretrain import ArgonneConfig, ArgonneModelParallel
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Register the model with Hugging Face's Auto classes
AutoConfig.register("argonne", ArgonneConfig)
AutoModel.register(ArgonneConfig, ArgonneModelParallel)
AutoModelForCausalLM.register(ArgonneConfig, ArgonneModelParallel)
def main():
# Load model and tokenizer using the Auto classes
model_dir = "PursuitOfDataScience/Argonne-1.0"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_dir)
# Setup for inference
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = model.to(device)
# Add the 'devices' attribute that model.generate() expects
if not hasattr(model, 'devices'):
model.devices = [device]
# Set up pipeline stages to None if model was loaded without distribution
if not hasattr(model, 'pipeline_stages') or model.pipeline_stages is None:
model.pipeline_stages = None
# Generate text from a prompt
prompt = "The future of AI research is "
# Extract just the input_ids from tokenizer output
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.to(device)
# Generate text
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_new_tokens=100,
temperature=0.7,
top_k=50
)
# Print the result
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"Generated text:\n{generated_text}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
📝 Example Outputs
Below are generated examples illustrating Argonne-1.0's style and capability when prompted:
Prompt: "The meaning of life is..."
The meaning of life is tantamount to an inescapable reality. It can be seen as an inescapable reality where life is lived in a vacuum, or a mere absence of life. Life can be considered as the ultimate reality, where life is no more, where life has no purpose, and life has no meaning.
Life is a form of art, rather than a mere collection or an endless expanse. It is a realm where art, music, philosophy, philosophy, and science come together to create something new, beautiful, and meaningful. It is the boundlessness of existence that creates the essence of art, music, philosophy and science.
So, what does a life mean? It means something
Prompt: "In the future, artificial intelligence will..."
In the future, artificial intelligence will tame the need for new ways to understand and control our lives. AI is already being used to do tasks that previously took human intelligence. But is it possible to predict what will come in the future, what will happen in the future, and how much will we be willing to pay for AI?
Evolutionary scientists have been developing new technologies that can be used to create artificial intelligence. For example, AI algorithms can be used to detect objects in a scene. These algorithms have been used in the design and manufacturing of many different products.
Similarly, AI algorithms can be used to predict the future by analyzing historical data and patterns in it. This information can be used to predict the future and make predictions accordingly.
- Downloads last month
- 23