problem
stringlengths 2
6.28k
| solution
stringlengths 0
13.5k
| answer
stringlengths 1
97
| problem_type
stringclasses 9
values | question_type
stringclasses 5
values | problem_is_valid
stringclasses 5
values | solution_is_valid
stringclasses 4
values | source
stringclasses 8
values | synthetic
bool 1
class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1. (10 points). Tourist Nikolai Petrovich was late by $\Delta t=5$ minutes for the departure of his riverboat, which had set off downstream. Fortunately, the owner of a fast motorboat agreed to help Nikolai Petrovich. Catching up with the riverboat and disembarking the unlucky tourist, the motorboat immediately set off on its return journey. How much time passed from the departure of the motorboat until its return? Assume that the speed of the riverboat relative to the water is $k=3$ times the speed of the river current, and the speed of the motorboat is $n=5$ times the speed of the river current. | 1. $s=\left(3 v_{\mathrm{T}}+v_{\mathrm{T}}\right) \cdot\left(t_{1}+\Delta t\right)=\left(5 v_{\mathrm{T}}+v_{\mathrm{T}}\right) \cdot t_{1} \rightarrow 4 \Delta t=2 t_{1} \rightarrow t_{1}=2 \Delta t=10$ min $t_{2}=\frac{s}{5 v_{\mathrm{T}}-v_{\mathrm{T}}}=\frac{6 v_{\mathrm{T}} \cdot t_{1}}{4 v_{\mathrm{T}}}=\frac{3}{2} t_{1}=3 \Delta t=15$ min $\rightarrow$ $T=t_{1}+t_{2}=5 \Delta t=25$ min | 25 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. (10 points). Three small metal spheres, one with radius $R$ and two with radius $2R$, are charged with the same charge $+q$ and are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with a side length significantly exceeding the radii of the spheres. The spheres are connected by a wire, and then the wire is removed. Find the ratio of the forces acting on the small sphere before and after the connection? | # 1.5 From eight identical segments of homogeneous wire of the same cross-section, a regular tetrahedral pyramid $A B C D F . \mathrm{K}$ was constructed. A source of constant voltage was connected to its vertices $A$ and $B$. Find the ratio of the thermal powers dissipated in the edges $A F$ and $C F$. By dividing the vertex node $F$ into two: from the symmetry of the circuit, their potentials will be equal to each other. The resistance $R_{A D F C} \equiv R_{1}$ of the upper part of the circuit $R_{1}=$ $\left(1+\frac{2 \cdot 1}{2+1}+1\right) R=\frac{8}{3} R$, where $R$ is the resistance of each edge separately.
$R_{2} \equiv R_{A F B}=\frac{2}{3} R$ - the resistance of the lower part of the circuit. $\frac{R_{1}}{R_{2}}=4$, therefore $\frac{I_{2}}{I_{1}}=\frac{1}{4}$.
The currents flowing in the edges $A F$ and $C F$ constitute the same fractions of $I_{1}$ and $I_{2}$, respectively, so $\frac{I_{C F}}{I_{A F}}=\frac{1}{4}$. Power is proportional to the square of the current $\left(P=I^{2} R\right)$, hence:
$$
\frac{P_{A F}}{P_{C F}}=16
$$ | 16 | Other | math-word-problem | Yes | Incomplete | olympiads | false |
2. (15 points) A satellite is launched vertically from the pole of the Earth at the first cosmic speed. To what maximum distance from the Earth's surface will the satellite travel? (The acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface $g=10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{c}^{2}$, radius of the Earth $R=6400$ km). | 2.
According to the law of conservation of energy: $\frac{m v_{I}^{2}}{2}-\frac{\gamma m M}{R}=-\frac{\gamma m M}{R+H}$
The first cosmic speed $v_{I}=\sqrt{g R}$
The acceleration due to gravity at the surface $g=\frac{\gamma M}{R^{2}}$
Then $\frac{m g R}{2}-m g R=-\frac{m g R^{2}}{R+H}$
Finally, $H=R=6400$ km.
(15 points) | 6400 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
6. (15 points) Looking down from the edge of the stream bank, Vovochka decided that the height of his rubber boots would be enough to cross the stream. However, after crossing, Vovochka got his legs wet up to his knees ($H=52$ cm). Estimate the height $h$ of Vovochka's boots. Assume the depth of the stream is constant, and the refractive index of water $n=1.33$.
Rector of SPbPU

A.I. Rudskoy S.A. Staroytov
## Instructions for Evaluating Final Round Solutions of the Polytechnic Physics Olympiad
The version given to the participant contains 6 problems of varying difficulty.
The evaluation of the work is based on the points received for each individual problem.
The score for solving each problem in the version is one of the following coefficients:
1.0 - the problem is solved correctly;
0.8 - the problem is solved correctly and the answer is given in a general form; there is an error in the unit of measurement of the obtained physical quantity or an arithmetic error;
0.6 - the problem is not fully solved; all necessary physical relationships for solving the problem are present; there is an error in algebraic transformations;
0.4 - the problem is not fully solved; some physical relationships necessary for solving the problem are missing;
0.2 - the problem is not solved; the work contains only some notes related to solving the problem or describing the phenomenon considered in the problem;
0.0 - the solution to the problem or any notes related to it are absent in the work.
The coefficient is entered in the first column "For the Teacher" of the "Answer Sheet". In the second column of the section, the score is entered, which is the product of the coefficient received for the solution and the maximum score for the given problem.
The obtained scores are summed and entered in the "Total" row.
Table for converting coefficients to points.
| \multirow{coefficient}{max points}{} | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
| 1 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| 0.8 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 |
| 0.6 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 |
| 0.4 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| 0.2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 6. From the figure
$\frac{d}{h}=\operatorname{tg} \alpha ; \quad \frac{d}{H}=\operatorname{tg} \beta ; \quad \frac{H}{h}=\frac{\operatorname{tg} \alpha}{\operatorname{tg} \beta}$
Since all the information about the bottom of the stream falls into the space limited by the eye's pupil, all angles are small: $\operatorname{tg} \alpha \approx \sin \alpha ; \operatorname{tg} \beta \approx \sin \beta$
Then $\frac{H}{h}=\frac{\sin \alpha}{\sin \beta}=n$
$h=\frac{H}{n}=39 \mathrm{~cm}$.
(15 points) | 39 | Other | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Dmitry is three times as old as Grigory was when Dmitry was as old as Grigory is now. When Grigory becomes as old as Dmitry is now, the sum of their ages will be 49 years. How old is Grigory? | Solution: Let Gregory be $y$ years old in the past, and Dmitry be $x$ years old. Then currently, Gregory is $x$ years old, and Dmitry is $3 y$ years old. In the future, Gregory will be $3 y$ years old, and Dmitry will be $z$ years old, and according to the condition, $z+3 y=49$. Since $z-3 y=3 y-x ; 3 y-x=x-y$, then $9 y-x=49$ and $x=2 y$. From this, we get that $x=14, y=7$. Currently, Gregory is 14 years old. Answer: 14. | 14 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. Solve the equation $\frac{4}{\sqrt{\log _{3}(81 x)}+\sqrt{\log _{3} x}}+\sqrt{\log _{3} x}=3$. | Solution: Using the properties of logarithms, our equation can be rewritten as $\frac{4}{\sqrt{4+\log _{3} x}+\sqrt{\log _{3} x}}+\sqrt{\log _{3} x}=3$. Let $t=\log _{3} x$. Then $\frac{4}{\sqrt{4+t}+\sqrt{t}}+\sqrt{t}=3$. Multiplying the numerator and denominator of the first fraction by $\sqrt{t+4}-\sqrt{t}$, we arrive at the equation $\sqrt{t+4}=3$. From this, we get that $t=5$ and $x=3^{5}=243$. Answer: 243. | 243 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
8. On the sides $B C, C A, A B$ of an equilateral triangle $A B C$ with side length 7, points $A_{1}, B_{1}, C_{1}$ are taken respectively. It is known that $A C_{1}=B A_{1}=C B_{1}=3$. Find the ratio of the area of triangle $A B C$ to the area of the triangle formed by the lines $A A_{1}, B B_{1}, C C_{1}$. | Solution:
Triangles $A B A_{1}, B C B_{1}, C A C_{1}$ are equal by sides and the angle between them, triangles $A D C_{1}, B E A_{1}, C F B_{1}$ are equal by side and angles. Triangle $A D C_{1}$ is similar to $A B A_{1}$ by two angles, triangle $A B C$ is similar to $D E F$. Let $S=S_{A B C}, S_{1}=S_{A B A_{1}}, S_{2}=S_{A C_{1} D}, S_{0}=S_{D E F} \cdot$ Then
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \qquad A A_{1}=\sqrt{A B^{2}+B A_{1}^{2}-2 A B \cdot B C_{1} \cos 60^{\circ}}=\sqrt{49+9-21}=\sqrt{37} \\
& \frac{S_{2}}{S_{1}}=\left(\frac{A C_{1}}{A A_{1}}\right)^{2}=\frac{9}{37}, \frac{S_{1}}{S}=\frac{B A_{1}}{B C}=\frac{3}{7} \\
& S_{0}=S-3 S_{1}+3 S_{2}=S-3 \cdot \frac{3}{7} S+3 \cdot \frac{9}{37} \cdot \frac{3}{7} S=\frac{S}{37}, \frac{S}{S_{0}}=37 \\
& \text { answer: } 37 \text {. }
\end{aligned}
$$
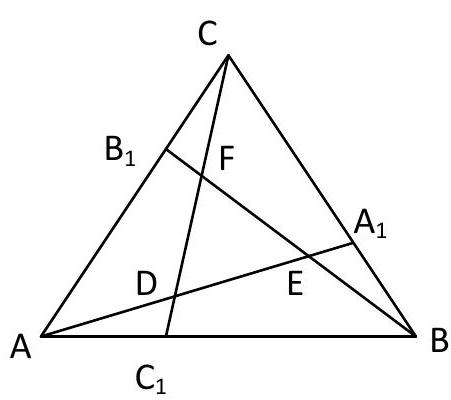 | 37 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Ivan is twice as old as Peter was when Ivan was as old as Peter is now. When Peter becomes as old as Ivan is now, the sum of their ages will be 54 years. How old is Peter? | Solution: Let Peter's age in the past be $y$ years, and Ivan's age be $x$ years. Then currently, Peter is $x$ years old, and Ivan is $2 y$ years old. In the future, Peter will be $2 y$ years old, and Ivan will be $z$ years old, and according to the condition, $z+2 y=54$. Since $z-2 y=2 y-x ; 2 y-x=x-y$, then $6 y-x=54$ and $2 x=3 y$. From this, we get that $x=18$. Currently, Peter is 18 years old. Answer: 18. | 18 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. Solve the equation $\frac{1}{\sqrt{\log _{5}(5 x)}+\sqrt{\log _{5} x}}+\sqrt{\log _{5} x}=2$. | Solution: Using the properties of logarithms, our equation can be rewritten as $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\log _{5} x}+\sqrt{\log _{5} x}}+\sqrt{\log _{5} x}=2$. Let $t=\log _{5} x$. Then $\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+t}+\sqrt{t}}+\sqrt{t}=2$. By multiplying the numerator and denominator of the first fraction by $\sqrt{t+1}-\sqrt{t}$, we arrive at the equation $\sqrt{t+1}=2$. From this, we get that $t=3$, so $x=5^{3}=125$. Answer: 125. | 125 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
8. On the sides $B C, C A, A B$ of an equilateral triangle $A B C$ with side length 11, points $A_{1}, B_{1}, C_{1}$ are taken respectively. It is known that $A C_{1}=B A_{1}=C B_{1}=5$. Find the ratio of the area of triangle $A B C$ to the area of the triangle formed by the lines $A A_{1}, B B_{1}, C C_{1}$. | Solution:
Triangles $A B A_{1}, B C B_{1}, C A C_{1}$ are equal by sides and the angle between them, triangles $A D C_{1}, B E A_{1}, C F B_{1}$ are equal by side and angles. Triangle $A D C_{1}$ is similar to $A B A_{1}$ by two angles, triangle $A B C$ is similar to $D E F$. Let $S=S_{A B C}, S_{1}=S_{A B A_{1}}, S_{2}=S_{A C_{1} D}$,
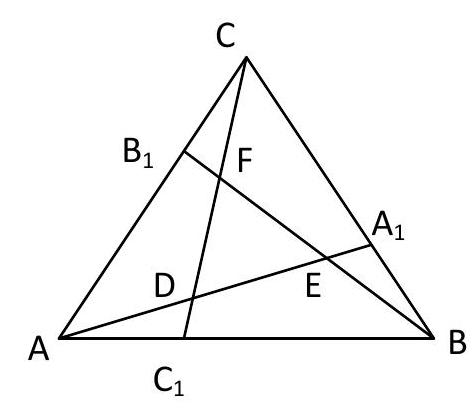
$S_{0}=S_{\text {DEF }} \cdot$ Then
$A A_{1}=\sqrt{A B^{2}+B A_{1}^{2}-2 A B \cdot B C_{1} \cos 60^{\circ}}=\sqrt{91}$,
$$
\frac{S_{2}}{S_{1}}=\left(\frac{A C_{1}}{A A_{1}}\right)^{2}=\frac{25}{91}, \frac{S_{1}}{S}=\frac{B A_{1}}{B C}=\frac{5}{11}
$$
$S_{0}=S-3 S_{1}+3 S_{2}=S-3 \cdot \frac{5}{11} S+3 \cdot \frac{25}{91} \cdot \frac{5}{11} S=\frac{S}{91}, \frac{S}{S_{0}}=91$.
Answer: 91. | 91 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
10. For what values of the parameter $a$ does the equation $x^{4}-40 x^{2}+144=a\left(x^{2}+4 x-12\right)$ have exactly three distinct solutions? | Solution: Factorize the right and left sides of the equation:
$(x-2)(x+2)(x-6)(x+6)=a(x-2)(x+6)$. The equation can be written as
$(x-2)(x+6)\left(x^{2}-4 x-12-a\right)=0$. It is obvious that 2 and -6 are roots of this equation. We are satisfied with the situation where exactly one of the roots of the equation $x^{2}-4 x-12-a=0$ does not coincide with 2 and -6. The total number of solutions will be three if the last equation has one root $x_{3}$, such that $x_{3} \neq x_{1}, x_{3} \neq x_{2}$, or if this equation has two roots $x_{3}, x_{4}$, one of which coincides with $x_{1}$ or $x_{2}$.
The equation $x^{2}-4 x-12-a=0$ has one root when $a=-16$ and this root coincides with 2. This case does not suit us. The number 2 is a root of this equation when $a=-16$. This case has already been considered. The number -6 is a root of this equation when $a=48$, and in this case, the second root is different from 2 and -6 - Answer: $a=48$. | 48 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 12. Task 12
In the insurance contract, the insurance amount is set at 500,000 rubles and a conditional franchise of $1 \%$. The actual damage amounted to 4000 rubles. What will be the amount of insurance compensation? | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement and any signs.
# | 3960 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 13. Problem 13
Maxim deposited 1000 rubles in a bank for a term of 1 year at an annual interest rate of $12 \%$ with monthly capitalization of interest. After one month, he closed his bank deposit. How much money will Maxim receive? | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement and any signs.
# | 1010 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 20. Problem 20
With a monthly income of 30000 rubles, mandatory monthly expenses for food amount to 15000 rubles, for utilities - 5000 rubles, and for phone, internet, and transportation costs - 2500 rubles. Having savings of 10000 rubles, it is planned to buy a new TV for 25000 rubles. In how many months can the TV be purchased without using borrowed funds? | Answer in the form of a number shouldbewrittenwithoutspaces,withoutunitsofmeasurementandanycharacters. | 5 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
From channel A to the Wiki site, $850 * 0.06=51$ people will transition
From channel B to the Wiki site, $1500 * 0.042=63$ people will transition
From channel C to the Wiki site, $4536 / 72=63$ people will transition | Answer: The most people will transition from channels B and V - 63 people each
## 2
Cost of transition from advertising on channel A: $-3417 / 51 = 67$ rubles
Cost of transition from advertising on channel B: $4914 / 63 = 78$ rubles
Answer: The lowest cost of transition to the site from advertising on channel A - 67 rubles
## 3
Number of sales after advertising on channel A: $51 * 0.05 = 2.55$ - round to 2 sales (by number of people)
Revenue from sales minus advertising expenses: $(2 * 2500) - 3417 = 1583$ rubles
Number of sales after advertising on channel B: $63 * 0.05 = 3.15$ - round to 3 sales (by number of people)
Revenue from sales minus advertising expenses: $(3 * 2500) - 4914 = 2586$ rubles
Number of sales after advertising on channel B: $63 * 0.05 = 3.15$ - round to 3 sales (by number of people)
Revenue from sales minus advertising expenses: $(3 * 2500) - 4536 = 2964$ rubles
Answer: Advertising on channel B will bring Vika the most profit. | 2964 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 15. Problem 15
In the insurance contract, an unconditional franchise of $1 \%$ of the damage amount is provided. The actual damage amounted to 300000 rubles. What will be the amount of insurance compensation? | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement and any signs.
# | 297000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 16. Problem 16
What is the amount of the mortgage loan a bank client will receive if their initial down payment is 2,000,000 rubles, and the loan amount is $75\%$ of the cost of the purchased property? | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement and any signs.
# | 8000000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
5.
Expenses for medical services provided to a child (under 18 years old) of the taxpayer by medical organizations
Correct answers: Pension contributions under a non-state pension agreement concluded by the taxpayer with a non-state pension fund in their own favor, Expenses for medical services provided to a child (under 18 years old) of the taxpayer by medical organizations, Expenses for their own education
Question 11
Score: 6.00
An investor has a brokerage account with an investment company. In 2021, the investor received the following income from securities:
- dividends on shares of JSC “Winning” amounted to 50,000 rubles;
- coupon income from government bonds OFZ amounted to 40,000 rubles;
- coupon income from corporate bonds of JSC “Reliable” amounted to 30,000 rubles.
In addition, the investor received a capital gain from selling 100 shares of JSC “Risky” at 200 rubles per share. The purchase price of 1 share was 150 rubles. The investor held the shares for 4 months.
The investor's salary for 2021 before taxation amounted to 1,000,000 rubles.
2022 Higher Trial - qualifying stage
rubles.
Calculate the amount of personal income tax (NDFL) on income from securities. | Answer and write it in rubles as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 16250
Question 12
Score: 5.00
Insert the missing terms from the drop-down list.
Under the insurance contract, one party
insured; insurance premium; beneficiary; insurer; insurance amount
undertakes to pay the other party
insured; insurance premium; beneficiary; insurer; insurance amount
in the event of an occurrence of an event provided for in the contract (insurance event) to compensate the other party
insured; insurance premium; beneficiary; insurer; insurance amount
or any other person in whose favor the contract is concluded
insured; insurance premium; beneficiary; insurer; insurance amount
, for losses caused by this event (pay insurance compensation) within the amount determined by the contract insured; insurance premium; beneficiary; insurer; insurance amount
Correct answer:
Insert the missing terms from the drop-down list.
Under the insurance contract, one party [insurer] undertakes to pay the other party [insurance premium] in the event of an occurrence of an event provided for in the contract (insurance event) to compensate the other party [insured] or any other person in whose favor the contract is concluded [beneficiary], for losses caused by this event (pay insurance compensation) within the amount determined by the contract [insurance amount].
Question 13
Score: 3.00
Mark all correct statements.
Owners of a voluntary life insurance policy are entitled to a tax deduction
Select one or more answers: | 16250 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
the higher the risk of a financial instrument, the higher its return
Correct answers: the higher the reliability of a financial instrument, the higher its return, a financial instrument can be reliable, profitable, and liquid at the same time, risk is not related to the return of a financial instrument
Question 15
Score: 6.00
Agnia's monthly salary in 2021 is 60,000 rubles (before taxation). It is known that on 01.01.2021, Agnia opened the following deposits in banks (she had no deposits before):
| Bank | Deposit amount, rub. | Interest rate, % per annum |
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
| A | 500,000 | 4.5 |
| B | 400,000 | 3.9 |
| C | 300,000 | 5.0 |
| C | 100,000 | 0.75 |
Interest on all these deposits is accrued and paid once at the end of the year. The key rate of the Bank of Russia on 01.01.21 was 4.25%. It is known that Agnia's total income for 2021 did not exceed 5,000,000 rubles. Calculate the amount of personal income tax (NDFL) Agnia should pay on the interest received in 2021. | Answer write in rubles as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 1378
Question 16
Score: 5.00
Establish the correspondence between specific taxes and their types.
| personal income tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| :---: | :---: |
| land tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| profit tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| property tax of individuals | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| transport tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
Correct answer:
personal income tax $\rightarrow$ federal tax,
land tax $\rightarrow$ local tax,
profit tax $\rightarrow$ federal tax,
property tax of individuals $\rightarrow$ local tax,
transport tax $\rightarrow$ regional tax
Question 17
Score: 6.00
Kirill wants to buy a TV costing 30000 rubles on credit. The bank offers him the necessary amount on loan with the condition that the borrowed amount must be repaid in three equal monthly installments. At the end of each month, interest must also be paid on the remaining debt, calculated at an annual rate of $18 \%$. Calculate the percentage of overpayment by Kirill from the loan amount.
Answer write in percentages as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer:
Correct answer: 3
Question 18
Score: 6.00
An investor has accumulated 400000 rubles and deposited them in a bank for 7 months at an annual interest rate of $6 \%$. Interest is compounded monthly. Calculate the amount of interest the investor will receive upon closing the deposit.
Answer write in rubles as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 14212
Question 19
Score: 3.00
Mark all correct statements.
If a bank, which is your counterparty, has its license revoked, then
Select one or more answers: | 1378 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4.
it is not necessary to pay off a credit taken in it
2022 Higher Trial - qualifying stage
5
offset can be made on a credit taken in it using your funds on deposit in the same bank
Correct answers: insurance compensation under the state deposit insurance system can only be paid in Russian rubles, compensation for a deposit under the state deposit insurance system can be received in cash or non-cash form, funds invested in the bank's securities can be recovered during the bankruptcy proceedings (liquidation)
Question 20
Score: 6.00
Alice invests her funds in a financial instrument with a nominal yield of $16 \%$ per annum. Inflation for the year was $6 \%$. Calculate the real return on investments in percentages using the exact Fisher formula. | Write the answer as a whole number without spaces and units of measurement
Answer:
The correct answer is9 | 9 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Incomplete | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 12. Problem 12
Sergei deposited 15 thousand rubles in a bank for 3 months at an annual interest rate of $6 \%$ with monthly capitalization of interest. What additional amount will he receive on top of the deposited funds? | Roundtothenearestwholenumber,recordwithoutspaces,unitsandanycharacters.
# | 228 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 14. Problem 14
Calculate the cadastral value of a land plot with an area of 11 acres, if the amount of tax paid amounted to 3300 rubles (tax rate $0.3 \%$) | Roundtothenearestwholenumber,recordwithoutspaces,unitsandanycharacters.
# | 11000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 17. Problem 17
Petr decided to deposit 500 thousand rubles in a bank account at an annual interest rate of 7% to save money for his retirement in 20 years. What amount will accumulate in the account by the time Petr retires, if the contract stipulates that interest is calculated annually using the simple interest formula. | Roundtothenearestwholenumber,writeitwithoutspaces,units,andanysigns.
# | 1700000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 18. Problem 18
The company issued 120 thousand ordinary shares with a nominal value of 1 ruble, as well as 10 thousand preferred shares with a nominal value of 3 rubles. As of the current date, the market price of an ordinary share is 30 rubles, and the market price of a preferred share is 35 rubles. Determine the size of the company's authorized capital. | Roundtothenearestwholenumber,writeitwithoutspaces,units,andanysigns.
# | 150000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 15. Problem 15
What amount of mortgage credit in rubles will a bank client receive if their initial payment of 1800000 rubles amounted to $30 \%$ of the cost of the purchased property? | Answer in the form of a number should bewrittenwithoutspaces,withoutunitsofmeasurementandanycharacters.
## Answer: 4200000
# | 4200000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 14. Problem 14
Full score -6
A zero-coupon bond is redeemed at its nominal value of 1000 rubles in one year. Determine the market value of the bond if the market rate of return is $10 \%$ per annum. | Roundtothenearestwholenumber,writeitwithoutspaces,units,andanysigns.
# | 909 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 17. Problem 17
Full score -6
A sports store is running a promotion: "Any t-shirt for 300 rubles. With the purchase of two t-shirts - a 60% discount on the second one." How many rubles will you have to pay for the purchase of two t-shirts? | Writeyouranswerwithoutspaces,unitsandanycharacters.
# | 540 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 18. Problem 18
Full score -6
A citizen, upon retirement, purchased a land plot (10 acres) with a cadastral value of 1300000 rubles. Calculate the land tax he must pay (tax rate $0.3 \%$). | Writeyouranswerwithoutspaces,unitsandanycharacters.
# | 3900 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 20. Problem 20
Full score -9
A new cottage was damaged in a fire. According to the insurance policy, the house was insured for 500,000 rubles with an absolute deductible of 1% of the insurance damage amount. As a result of the fire, the foundation, valued at 50,000 rubles, and some metal structures, valued at 30,000 rubles, remained undamaged. The cost of removing debris is estimated at 10,000 rubles. What amount will the insured receive from the insurance company as insurance compensation? | Answerwithoutspaces,unitsofmeasurementandanycharacters. | 435000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
# 18. Problem 18
The owner of an apartment rents it out for five years and receives 240,000 rubles from tenants at the end of each year. The owner does not spend the rental income but saves it in a term deposit with an annual interest rate of $10\%$ (capitalization occurs once at the end of the year). What amount will the owner have in the account after five years? | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement, and without any symbols (rounding to the nearest whole number if necessary).
# | 159383 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 19. Problem 19
The owner of an apartment insured it for 3,750,000 rubles (the actual cost of the apartment is 7,500,000 rubles). The actual damage amounted to 2,750,000 rubles. The insurance compensation under the system of proportional liability was 1,350,000 rubles. Determine the amount of the absolute deductible provided for in the insurance contract: | Write the answer as a number without spaces, without units of measurement and any signs.
# | 1100000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
reducing transaction time
## Correct answers:
using licensed software, using a personal computer instead of a public one, using antivirus programs
Question 3
Balya: 7.00
Mr. Vshokoladov earned X rubles per month throughout 2021. In addition, during this year, he won 2000000 rubles in a lottery. What is $X$ if the total amount of personal income tax paid by Mr. Vshokoladov for this year was 1239480 rubles. | Answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer:
Correct answer: 600000
Question 4
Score: 3.00
Select all correct continuations of the statement.
2022 Higher Trial - qualifying stage
To file a petition to recognize a citizen as bankrupt...
## Select one or more answers:
\ulcorner | 600000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
A custodian stores securities, clients' money, and other material assets
Correct answers: A paid investment advisor consults and provides recommendations to the client on investment management, A trustee manages the client's property in their own name
Find the correspondence between the term and the statement so that all 5 pairs are correct. All 5 terms must be used.
The service may involve changing the terms of an existing loan
According to federal law, this service is available only once during the entire loan period
The service provides options for reducing the term or the amount of loan payments
During the term of this service, the bank does not charge the borrower penalties and cannot demand early repayment of the loan
This service may include
refinancing; consolidation of debts; loan holidays; mortgage holidays; early repayment; restructuring;
refinancing; loan holidays; mortgage holidays; early repayment; restructuring;
refinancing; loan holidays; mortgage holidays; early repayment; restructuring;
refinancing; loan holidays; mortgage holidays; early repayment; restructuring;
refinancing; loan holidays; mortgage holidays; early repayment; restructuring;
Correct answer:
The service may involve changing the terms of an existing loan $\rightarrow$ restructuring,
According to federal law, this service is available only once during the entire loan period $\rightarrow$ mortgage holidays,
The service provides options for reducing the term or the amount of loan payments $\rightarrow$ early repayment,
During the term of this service, the bank does not charge the borrower penalties and cannot demand early repayment of the loan $\rightarrow$ loan holidays, This service may include consolidation of debts $\rightarrow$ refinancing
Question 8
Score: 7.00
The Ivanov family carefully plans their budget. Lidia Nikolaevna works as a doctor and earns 1,000,000 rubles per year (before income tax). Arkady Petrovich is an entrepreneur, and his annual profit from the business is 2,000,000 rubles, which is taxed at a rate of $15 \%$ under the simplified taxation system (USN).
On average, the family's expenses amount to 205,000 rubles per month, excluding vacation expenses.
The Ivanovs had been saving money for a trip to Paris for a year, but due to the pandemic, they decided to postpone the trip for a year and temporarily place the accumulated savings in a bank deposit at an annual interest rate of $12 \%$ with interest paid at the end of each quarter. The deposit term is 12 months, and interest income is reinvested. Calculate the Ivanov family's income from the deposit. | Answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement. Round the answer to the nearest whole number according to rounding rules.
Answer:
Correct answer: 13806
question 9
Score: 3.00
Select all possible features of an authentic ruble banknote.
Select one or more answers:
$\Gamma$ | 13806 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
watermark
Correct answers: raised relief of certain text fragments, watermark, inscriptions and ornaments
Question 10
Score: 7.00
Vladimir has saved 16,500 rubles to buy a gaming console as a birthday gift for his brother, which amounts to 220 US dollars at the current exchange rate. The birthday is not until a month from now, and Vladimir is comparing three
Financial Literacy 11th Grade Day 1
alternatives: 1) buy the console now; 2) buy US dollars with the saved amount now, and convert them back to rubles in a month to buy the console; or 3) deposit 16,500 rubles in the bank now, with the condition that he will receive 16,665 rubles in a month, and then buy the chosen console.
Calculate the minimum exchange rate of US dollars at the end of the month for the second alternative to be economically beneficial for Vladimir. Assume that there are no bank fees or currency conversion fees. | Answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement. Round the answer to the nearest whole number according to rounding rules.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 76
Question 11
Score: 3.00
What services can currently be provided remotely? Select all appropriate options. | 76 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
the driver's marital status
Correct answers: bonus-malus coefficient, engine power, driver's age
Question 14
Score: 7.00
Maria Ivanovna has retired. She did not have a funded pension, only a social insurance pension, and her individual pension coefficient amount is 120. In addition, Maria Ivanovna has a bank deposit of 600,000 rubles, placed at an annual interest rate of $4 \%$ with monthly interest payments, which she does not reinvest but withdraws from the account monthly. How much money does Maria Ivanovna have available each month if the fixed part of her pension is 6050 rubles per month, and the cost of the pension coefficient is 99 rubles? | Provide the answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer:
The correct answer is: 19930
Question 15
Score: 7.00
Insert the missing words from the list below (not all provided words will be needed!):
Paying
credit; preferential; higher; cash withdrawal; service; blocking; bonus; debit; freeze; lower; transfer;
with a card, you spend the bank's funds, which you will have to return later.
If you do this before the end of the
credit; preferential; higher; cash withdrawal; service; blocking;
bonus; debit; freeze; lower; transfer;
period, the fee for using these funds is not charged, if you do not manage to, you will have to pay interest, which is usually significantly
credit; preferential; higher; cash withdrawal; service; blocking; bonus; debit; freeze; lower; transfer;
than the interest on a regular loan. In addition, the bank usually
charges interest for
credit; preferential; higher; cash withdrawal; service; blocking; bonus; debit; freeze; lower; transfer;
money from an ATM and an annual fee for
credit; preferential; higher; cash withdrawal; service; blocking;
bonus; debit; freeze; lower; transfer;
card.
Correct answer:
Insert the missing words from the list below (not all provided words will be needed!):
Paying [credit] card, you spend the bank's funds, which you will have to return later. If you do this before the end of the [preferential] period, the fee for using these funds is not charged, if you do not manage to - you will have to pay interest, which is usually significantly [higher] than the interest on a regular loan. In addition, the bank usually charges interest for [cash withdrawal] money from an ATM and an annual fee for
[service] card.
Question 16
Score: 3.00
In what cases is no commission charged for a transfer between individuals in Russia? Select all applicable answers.
Select one or more answers: | 19930 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
6.
when transferring money abroad
Correct answers: when using the Fast Payment System for amounts up to 100 thousand rubles per month, when transferring funds between one's own accounts in the same bank
Question 17
Score: 7.00
Last year, a beauty salon offered a $20 \%$ discount on facial massage when purchasing a membership for 30000 rubles. This year, it was decided to change the loyalty program and, when purchasing a membership for 30000 rubles, an additional $20 \%$ of this amount would be credited to the client's account. How will the number of facial massages that a client can now attend with a membership for 30000 rubles change, if the cost of a massage is 1500 rubles?
In the answer, write a non-negative integer without units of measurement. If the number of massages has not changed, put 0. | Answer:
The correct answer: 1
Question 18
Score: 3.00
Select all true statements regarding digital financial assets $(DFA)$.
Select one or more answers: | 1 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5.
The Bank of Russia will ensure the conversion of the "digital ruble" into another form of money (rubles) at a one-to-one ratio.
Correct answers: Stablecoins, backed by cash or gold, are an example of a CBDC., The Bank of Russia will ensure the conversion of the "digital ruble" into another form of money (rubles) at a one-to-one ratio.
Question 19
Score: 7.00
Angelika owns a commercial space of 30 sq. m. She wanted to organize a music club there and give piano lessons. But a friend offered Angelika a job as a manager in his company, and she decided to calculate which option would be more economically beneficial for her. If she opens the club, Angelika plans to choose a simplified tax system with a rate of $15 \%$ of the profit received, while her salary, which she spends entirely on monthly expenses, after paying personal income tax, will be 60,900 rubles per month.
Additional information:
rent rate: 12,000 rubles per 1 sq m per year, paid at the beginning of the year.
interest rate on a loan: $12 \%$ per year, with interest accrued at the end of the year interest rate on a deposit: $9 \%$ per year, with interest accrued at the end of the year Determine the minimum annual profit Angelika needs to achieve from the music club (before taxation) for this alternative to be economically beneficial for her. | Provide the answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement. Round the answer to the nearest whole number.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 1321412
Question 20
Score: 7.00
Financial Literacy 11th Grade Day 1
Ivan and Petr, twin brothers, went on a vacation by the sea together and purchased two different travel insurance policies, which also cover medical expenses during the trip. Ivan bought insurance for 450 rubles with a deductible of $25. Petr bought insurance for 500 rubles with no deductible. During the trip, the brothers fell ill and had to see a doctor, which cost $100 for each of them. Calculate how much more the brother who bought the less advantageous insurance policy paid compared to the other brother? Conduct calculations in rubles, using the exchange rate of 75 rubles per $. Provide the answer in rubles, without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer:
Correct answer: 1825 | 1321412 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. What amount of personal income tax refund over three years can Vasya receive if he chooses an investment tax deduction of type A (from investments in an IIS)? Provide a solution. | Solution: 200,000 * 0.13 * 3 = 78,000 rubles | 78000 | Other | math-word-problem | Incomplete | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 15. Problem 15
Full score -8
Grisha owns a room with an area of 9 m $^{2}$ in a communal apartment (its cadastral value is 1 million rubles, and the current market value is 1.5 million rubles), as well as a residential house with an area of $90 \mathrm{~m}^{2}$ (the cadastral value of the house is 1.8 million rubles, and its current market value is 2 million rubles).
If the property tax rate was the same for both objects and amounted to $0.1 \%$, how much should Grisha pay as property tax? | Give the answer in rubles and write it without spaces, units of measurement, and any signs.
# | 2700 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 16. Problem 16
Full score - 8
Dima wants to buy a car on the secondary market. To find a car and check its technical characteristics, he needs to spend three working days, taking leave at his own expense. If he buys a car without checking, he will have to spend approximately $20 \%$ of the car's cost on repairs. Dima's salary is 7000 rubles per day.
At what maximum car cost would Dima's decision to buy a car without checking be economically justified | Give the answer in rubles and write it without spaces, units of measurement, and any signs.
# | 140000 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
# 18. Problem 18
Full score -8
Genya needs to return 100,000 rubles to his friend right now, which he had previously borrowed. Initially, he wanted to use his term deposit (200,000 rubles for 3 months at 4% per annum, with all interest accrued at the end of the term; two months have already passed). However, under the terms of the deposit, if Genya withdraws money, either in full or in part, he will lose all interest on the deposit. Additionally, Genya learned that he would have to pay a commission of 1000 rubles for transferring money through the bank's personal account.
Therefore, Genya chose the second option: he used a free credit card from another bank, which offers a 60-day grace period and charges only 500 rubles for transferring 100,000 rubles. Genya settled the credit card debt after a month, when the term deposit matured.
How much more advantageous was the second option for Genya? | Answerinrubleswithroundingtothenearestinteger,recordwithoutspaces,withoutunitsofmeasurementandanycharacters.
# | 1050 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Incomplete | olympiads | false |
5.
the higher the risk of a financial instrument, the higher its return
Correct answers: the higher the reliability of a financial instrument, the higher its return, a financial instrument can be reliable, profitable, and liquid at the same time, risk is not related to the return of a financial instrument
Question 15
Score: 6.00
Agnia's monthly salary in 2021 is 60,000 rubles (before taxation). It is known that on 01.01.2021, Agnia opened the following deposits in banks (she had no deposits before):
| Bank | Deposit amount, rub. | Interest rate, % per annum |
| :---: | :---: | :---: |
| A | 500000 | 4.5 |
| B | 400000 | 3.9 |
| C | 300000 | 5.0 |
| C | 100000 | 0.75 |
Interest on all these deposits is accrued and paid once at the end of the year. The key rate of the Bank of Russia on 01.01.21 was 4.25%. It is known that Agnia's total income for 2021 did not exceed 5,000,000 rubles. Calculate the amount of personal income tax (NDFL) Agnia should pay on the interest received in 2021. | Answer write in rubles as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 1378
Question 16
Score: 5.00
Establish the correspondence between specific taxes and their types.
| personal income tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| :---: | :---: |
| land tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| profit tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| property tax of individuals | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
| transport tax | federal tax; local tax; regional tax; |
Correct answer:
personal income tax $\rightarrow$ federal tax,
land tax $\rightarrow$ local tax,
profit tax $\rightarrow$ federal tax,
property tax of individuals $\rightarrow$ local tax,
transport tax $\rightarrow$ regional tax
Question 17
Score: 6.00
Kirill wants to buy a TV costing 30000 rubles on credit. The bank offers him the necessary amount on loan with the condition that the borrowed amount must be repaid in three equal monthly installments. At the end of each month, interest must also be paid on the remaining debt, calculated at an annual rate of $18 \%$. Calculate the percentage of overpayment by Kirill from the loan amount.
Answer write in percentages as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer:
Correct answer: 3
Question 18
Score: 6.00
An investor has accumulated 400000 rubles and deposited them in a bank for 7 months at an annual interest rate of $6 \%$. Interest is compounded monthly. Calculate the amount of interest the investor will receive upon closing the deposit.
Answer write in rubles as an integer without spaces and units of measurement.
Answer: $\qquad$
Correct answer: 14212
Question 19
Score: 3.00
Mark all correct statements.
If a bank, which is your counterparty, has its license revoked, then
Select one or more answers: | 1378 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Task 1. Dad and Mom are cooking pancakes on the stove, while their children Petya and Vasya are eating them. Dad can cook 70 pancakes in an hour, and Mom can cook 100 pancakes. Petya, if he tries hard, can eat 10 pancakes in 15 minutes, and Vasya can eat twice as much. After how much time will there be no less than 20 uneaten pancakes left on the table? | Answer: 24 min
Solution. Let the baking rate of pancakes be $p_{1}=\frac{170}{60}$ pancakes/min, and the eating rate of pancakes be $p_{2}=\frac{10+20}{15}=2$ pancakes/min.
In $k$ minutes, there will be no less than $q=k\left(p_{1}-p_{2}\right)$ pancakes left on the table: $k \cdot \frac{5}{6} \geq 20 \rightarrow k \geq 24$. | 24 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Problem 2. In a square of grid paper containing an integer number of cells, a hole in the shape of a square, also consisting of an integer number of cells, was cut out. How many cells did the large square contain if 209 cells remained after the cutout? | Answer: 225 cells
Solution. The side of the larger square contains $n$ sides of a cell, and the side of the smaller square contains $m$ sides of a cell. Then $n^{2}-m^{2}=209 \rightarrow(n-m)(n+m)=209=11 \cdot 19$.
Case 1. $\left\{\begin{array}{c}n+m=209 \\ n-m=1\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}n=105 \\ m=104\end{array}\right.\right.$ case does not occur due to the absence of a hole
Case 2. $\left\{\begin{array}{l}n+m=19 \\ n-m=11\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}n=15 \\ m=4\end{array}\right.\right.$ | 225 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. (informatics) In a square matrix of size $N \times N$, all cells are filled with numbers from 1 to 5. A connected component in the matrix is defined as a set of cells that are filled with the same number, and between any two cells in the set, a path can be constructed. Cells can only be connected in a path if they are adjacent horizontally or vertically.
In other words, a connected component of the matrix is a connected shape, where the cells are filled with the same number.
For a given matrix, the task is to find the connected component consisting of the largest number of cells.
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
In the first line of the input data, there is an integer $N$ such that $1 \leq N \leq 10$. In the next $N$ lines, there are $N$ integers separated by spaces, each number is within the range from 1 to 5. The output should be a single number - the number of cells in the largest connected component of the matrix.
Examples of input data and program results:
| Example input data | | | | Example result | | |
| :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- | :--- |
| 6 | | | | | | |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 2 | |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 5 | |
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 | |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 5 | |
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | |
## Comments on the informatics problem:
The solution to the problem is a program code written in any traditional programming language, with the language specified. In the case of the impossibility of writing code in a traditional programming language, a correct algorithm of the program, presented in the form of a flowchart or pseudocode, can be accepted as a partial solution.
The program should read input data from the standard input stream (as if these data are entered from the keyboard) and output results to the standard output stream (as if these data are printed on the screen). The program should work correctly with the input data described in the problem conditions. The correctness of the input data is guaranteed, and it is not necessary to check it additionally within the program (if the problem states that an integer from 0 to 1000 is input, there is no need to additionally check whether, for example, a text string or a number outside this range is entered).
The program should output only the answer required by the problem (which may be accompanied by a brief textual formatting or without it). Any other output of results during the program's operation will be considered an error. For better understanding of the problem conditions and formats of input and output data, the problem is accompanied by several examples of correct input data and the correct result of the program's operation, provided in the section “examples of input data and program results”.
The written program should work efficiently, that is, compute the correct answer as quickly as possible. Programs that are written significantly inefficiently, that is, taking significantly more time than efficient solutions, will be considered an incomplete solution.
The program code should be written clearly, neatly, with indentation and a reasonable amount of comments in the program code. Minor syntactic errors in the code are allowed, provided that they do not affect the overall readability and understanding of the code. An untidy (unreadable) program code and/or a large number of syntactic errors may result in a reduced overall score for the problem.
## Example of solution formatting (program code):
```
{pascal} // indication of the language in which the program is written
program MyProg;
var:
begin
{read input data} // comment in the body of the program
readln (a,b);
..
{main body of the program}
*.
{output the answer}
writeln('The desired number: ',x);
end.
``` | # Solution.
program prog11;
var n,i,j,k,l:integer;
a,b:array[0..11,0..11] of integer;
m,mc,mmax:integer;
begin
{initialize the array}
for i:=0 to 11 do
for j:=0 to 11 do
```
a[i,j]:=0;
{read input data}
readln(N);
for i:=1 to N do
begin
for j:=1 to N do
read(a[i,j]);
readln;
end;
mmax:=0;{current value of the maximum component power}
{form a connected component from each element of the matrix}
for k:=1 to N do
for l:=1 to N do
begin
{initialize the auxiliary array}
for i:=0 to 11 do
for j:=0 to 11 do
b[i,j]:=0;
b[k,1]:=1;{add the first element of the component}
m:=1;{current component power}
mc:=1;{current increment power at the algorithm step}
while mc>0 do{while new elements were added on the previous step}
begin
mc:=0;
for i:=1 to N do
for j:=1 to N do
if (b[i,j]=0) then{element not added to the connected component}
if ((b[i,j-1]=1) and (a[i,j-1]=a[i,j]))
or ((b[i,j+1]=1) and (a[i,j+1]=a[i,j]))
or ((b[i-1,j]=1) and (a[i-1,j]=a[i,j]))
or ((b[i+1,j]=1) and (a[i+1,j]=a[i,j]))
then{there is a neighbor in the connected component and the cell values match}
begin {add the element to the connected component}
b[i,j]:=1;
inc(m);
```
inc(mc)
end;
end;
if m>mmax then mmax:=m; {check and update the maximum}
end;
writeln(mmax); {output the answer}
end. | 12 | Other | other | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Along one side of the road, there are 15 houses numbered $1,2, \ldots, 15$ (see figure). The residents of these houses travel to work on the road by bus. At a certain moment, one person from each house came out and headed to the bus stop. Indicate the house number where the bus stop should be built to minimize the average distance traveled by them? (mathematical problem: houses and the stop are points)
 | 1. The correct idea for solving the problem is the difference between the force of Archimedes acting on the hemisphere and the force of the liquid column pressure on its upper surface - 0.5 points | 8 | Logic and Puzzles | math-word-problem | Yes | Problem not solved | olympiads | false |
1. (mathematics) There are scales with two pans, 4 weights of 2 kg each, 3 weights of 3 kg each, and two weights of 5 kg each. In how many different ways can a 12 kg load be balanced on the scales, if the weights are allowed to be placed on both pans? | Answer: 7 ways
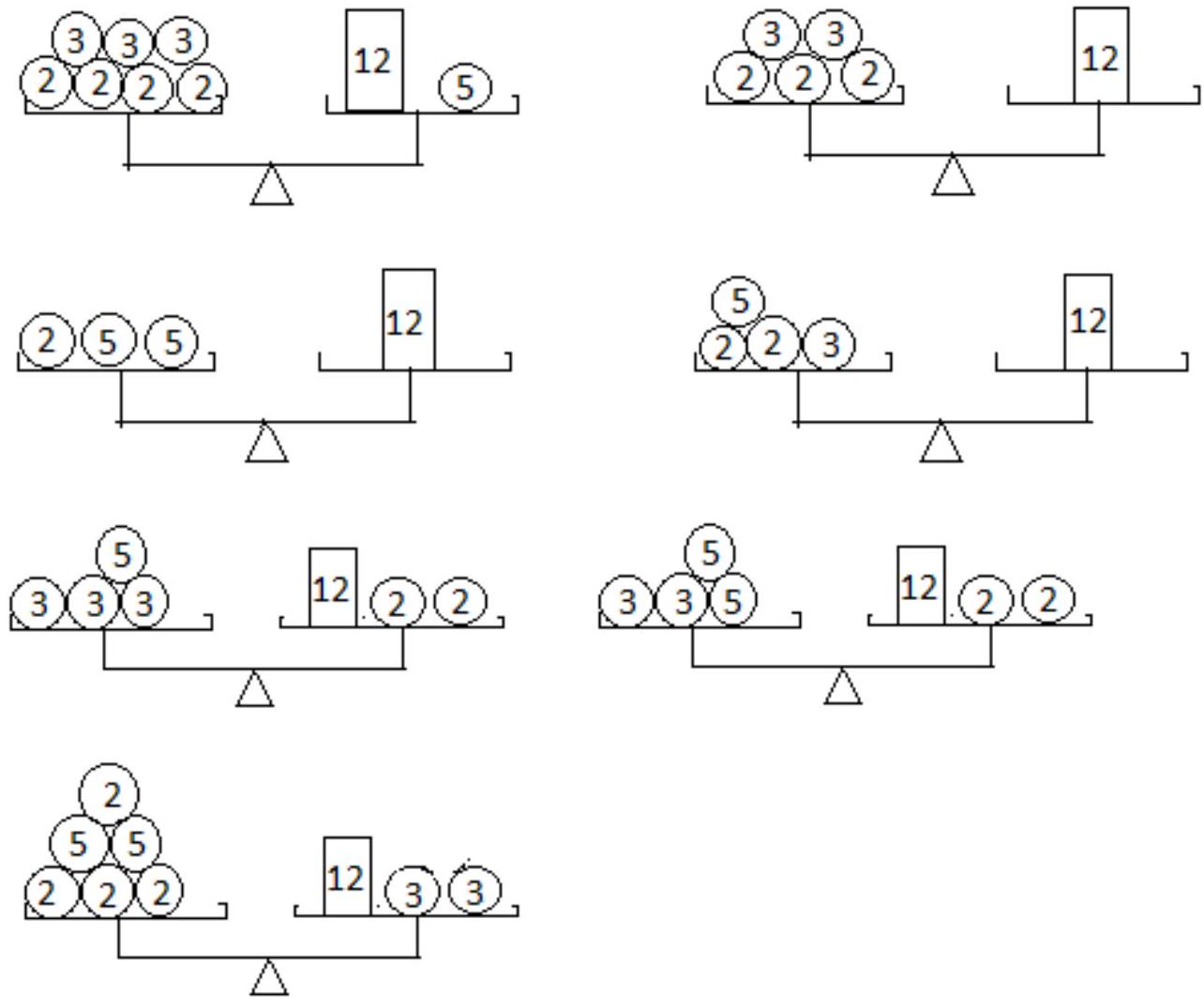
Solution: Let $x$ be the number of 2 kg weights used in weighing, $y$ be the number of 3 kg weights, and $z$ be the number of 5 kg weights. Then the equilibrium condition is given by
$$
\pm 2 x \pm 3 y \pm 5 z=12
$$
The plus sign before an unknown, for example $x$, means that the 2 kg weights are placed on the opposite pan from the 12 kg load. Otherwise, a minus sign is used. Keeping the same notation, we assume that $x, y$, and $z$ are integers that can take negative values, with $|x| \leq 4,|y| \leq 3,|z| \leq 2$. In this case, the equilibrium condition takes the form of the equation
$$
2 x+3 y+5 z=12
$$
Let $z=t \in[-2 ; 2]$. Then, solving the Diophantine equation,
$2 x+3 y=12-5 t \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=5 t-12-3 s \\ y=12-5 t+2 s, s \in Z\end{array}\right.$
Case 1. $t=-2$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=-22-3 s \\ y=22+2 s, s \in Z\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}|22+3 s| \leq 4 \rightarrow s=-8,-7,-6 \\ |22+2 s| \leq 3 \rightarrow s=-13,-12,-11,-10\end{array} \rightarrow s \in \varnothing\right.\right.$
Case 2. $t=-1$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=-17-3 s \\ y=17+2 s, s \in Z\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}|17+3 s| \leq 4 \rightarrow s=-5,-6,-7 \\ |17+2 s| \leq 3 \rightarrow s=-7,-8,-9,-10\end{array} \rightarrow s_{1}=-7 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=4 \\ y=3 \\ z=-1\end{array}\right.\right.\right.$
Case 3. $t=0$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=-12-3 s \\ y=12+2 s, s \in Z\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}|12+3 s| \leq 4 \rightarrow s=-5,-4,-3 \\ |12+2 s| \leq 3 \rightarrow s=-7,-6,-5\end{array} \rightarrow s_{2}=-5 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}x=3 \\ y=2 \\ z=0\end{array}\right.\right.\right.$
Case 4. $t=1$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=-7-3 s \\ y=7+2 s, s \in Z\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}|7+3 s| \leq 4 \rightarrow s=-1,-2,-3 \\ |7+2 s| \leq 3 \rightarrow s=-2,-3,-4,-5\end{array} \rightarrow s_{3}=-2 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}x=-1 \\ y=3, s_{4}=-3 \\ z=1\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}x=2 \\ y=1 \\ z=1\end{array}\right.\right.\right.\right.$
Case 5. $t=2$
$\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=-2-3 s \\ y=2+2 s, s \in Z\end{array} \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}|2+3 s| \leq 4 \rightarrow s=0,-1,-2 \\ |2+2 s| \leq 3 \rightarrow s=0,-1,-2\end{array} \rightarrow s_{5}=0 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}x=-2 \\ y=2,2 \\ z=2\end{array},-1 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{l}x=1 \\ y=0 \\ z=2\end{array}\right.\right.\right.\right.$
$s_{7}=-2 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=4 \\ y=-2 \\ z=2\end{array}\right.$ | 7 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Express z from the first equation and substitute into the second:
$x^{2}-2 x+y^{2}-2 \sqrt{3} y=-4 \rightarrow(x-1)^{2}+(y-\sqrt{3})^{2}=0 \rightarrow\left\{\begin{array}{c}x=1 \\ y=\sqrt{3}\end{array} \rightarrow z=x^{2}+y^{2}+2 x=6\right.$ | Answer: $x=1, y=\sqrt{3}, z=6$ | 6 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Task 1. The administration divided the region into several districts based on the principle: the population of a large district exceeds $8 \%$ of the region's population and for any large district, there are two non-large districts with a combined population that is larger. Into what minimum number of districts was the region divided? | Answer: 8 districts.
Solution. The number of "small" districts is no less than 2 according to the condition, and their population does not exceed $8 \%$ of the total population of the region. We will show that the number of districts in the region is no less than 8. If the number of districts in the region is no more than 7, but there are no more than 5 "large" districts with a population of less than $16 \%$ each. Then the total population of the region cannot amount to $100 \%$. Indeed, $2 \cdot 8 \%+5 \cdot 16 \%=96 \%<100 \%$. Thus, the number of districts in the region is no less than 8. A division into 8 districts is possible, for example, $8 \%+8 \%+14 \%+14 \%+14 \%+14 \%+14 \%+14 \%=100 \%$. | 8 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Problem 3. Point $M$ is located on side $CD$ of a square such that $CM: MD=1: 3$. Line $AM$ intersects the circumcircle of the square at point $E$. The area of triangle $ACE$ is 14. Find the side length of the square. | Answer: 10.
Solution.
Triangles $A M D$ and $C M E$ are similar with a similarity coefficient $k=5$. Then
$$
C E=\frac{4 x}{5}, M E=\frac{3 x}{5} \rightarrow A E=5 x+\frac{3 x}{5}=\frac{28}{5} x
$$
Triangle $A C E$ is a right triangle, therefore:
$$
S_{A C E}=\frac{1}{2} A E \cdot C E=\frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{28}{5} \cdot \frac{4}{5} x^{2}=14 \rightarrow x^{2}=\frac{25}{4} \rightarrow x=\frac{5}{2} \rightarrow A D=4 x=10
$$ | 10 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Problem 1. Seven students in the class receive one two every two days of study, and nine other students receive one two every three days each. The rest of the students in the class never receive twos. From Monday to Friday, 30 new twos appeared in the journal. How many new twos will appear in the class journal on Saturday? | Answer: 9
Solution. Over the period from Monday to Saturday (six days), in the journal, there will be 3 new twos from each student of the first group (seven people) and 2 new twos from each of the 9 students of the second group. The total number of new twos for the school week is $7 \cdot 3 + 9 \cdot 2 = 39$. Then, on Saturday, the journal will have $39 - 30 = 9$ new twos. | 9 | Logic and Puzzles | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Problem 3. Through the vertex $B$ of an equilateral triangle $ABC$, a line $L$ is drawn, intersecting the extension of side $AC$ beyond point $C$. On line $L$, segments $BM$ and $BN$ are laid out, each equal in length to the side of triangle $ABC$. The lines $MC$ and $NA$ intersect at a common point $D$ and intersect the sides $AB$ and $BC$ of the triangle at points $P$ and $Q$ respectively. Prove that a circle can be circumscribed around quadrilateral $PBQD$. Find the radius of this circle if the length of segment $PQ$ is $\sqrt{3}$. | # Answer: 1.
Solution. Triangles $M B C$ and $A B N$ are isosceles, therefore
$$
\begin{gathered}
\angle B M C = \angle B C M = \alpha \rightarrow \angle N B C = 2 \alpha, \angle B A N = \angle B N A = \beta \rightarrow \angle A B M = 2 \beta \\
2 \alpha + 2 \beta + 60^{\circ} = 180^{\circ} \rightarrow \alpha + \beta = 60^{\circ}
\end{gathered}
$$
In triangle $M D N$, angle $P D Q$ is $180^{\circ} - \alpha - \beta = 120^{\circ}$, and the sum of the opposite angles of quadrilateral $P B Q D$ is $180^{\circ}$, so a circle can be circumscribed around it.
By the Law of Sines, $P Q = 2 R \sin 120^{\circ} = \sqrt{3} \rightarrow R = 1$. | 1 | Geometry | proof | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Answer: 125 cm, 75 cm
# | # Solution

Notations:
$$
\vec{c}=\overrightarrow{O Q} \quad \vec{a}=\overrightarrow{O A} \quad \vec{b}=\overrightarrow{Q B}
$$
Then $\vec{c}+(\vec{b}-\vec{a})=\overrightarrow{A B}$. The problem requires finding the greatest and smallest possible length of the vector $\overrightarrow{A B}$. The vector $\vec{c}$ is constant (unchanging over time) and has a length of 100 cm. The vectors $\vec{a}$ and $\vec{b}$ are perpendicular at any moment by the condition, and the vector $\vec{b}-\vec{a}$, which has a constant length of $\sqrt{15^{2}+20^{2}}=25$ cm and its origin at point $O$, rotates around point $O$ with a constant angular velocity. The vector $\overrightarrow{A B}$ has its maximum and minimum length when the vectors $\vec{c}$ and $\vec{b}-\vec{a}$ are collinear. $|\overrightarrow{A B}|_{\min }=100-25=75,|\overrightarrow{A B}|_{\max }=100+25=125$
Answer: 125 cm, 75 cm | 125 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Incomplete | Yes | olympiads | false |
16. The last digit of a six-digit number was moved to the beginning (for example, $456789 \rightarrow$ 945678), and the resulting six-digit number was added to the original number. Which numbers from the interval param 1 could have resulted from the addition? In the answer, write the sum of the obtained numbers.
| param1 | Answer |
| :---: | :---: |
| $[891870 ; 891899]$ | |
| $[375355 ; 375380]$ | |
| $[427411 ; 427434]$ | |
| $[639619 ; 639647]$ | | | 16. The last digit of a six-digit number was moved to the beginning (for example, $456789 \rightarrow$ 945678), and the resulting six-digit number was added to the original number. Which numbers from the interval param 1 could have resulted from the addition? In the answer, write the sum of the obtained numbers.
| param1 | Answer |
| :---: | :---: |
| $[891870 ; 891899]$ | 1783771 |
| $[375355 ; 375380]$ | 750739 |
| $[427411 ; 427434]$ | 854843 |
| $[639619 ; 639647]$ | 1279267 | | 1279267 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+11 x+23$. | Answer: 22.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+11 x+23>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{4}(x+2)(x-46)>0$, from which $-2<x<46$. On this interval, there are 45 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=45$. In this interval, $y$ takes integer values only for even $x$ - a total of 22 possibilities. Thus, we get 22 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 22 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 * 2 *$, each of the 6 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 12-digit number is divisible by 45. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 13122.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 45, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 5 and by 9. To ensure divisibility by 5, we can choose 0 or 5 as the last digit (2 ways).
To ensure divisibility by nine, we proceed as follows. We will choose four digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9$ ways), and then select the fifth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 9. Since these digits give all possible remainders when divided by $9 (0,1,2, \ldots, 8)$, and each remainder occurs exactly once, the last digit can be chosen in one way.
Applying the rule of product, we get that the total number of ways is $2 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 1=13122$. | 13122 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane that have natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lie on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+3 x+\frac{253}{4}$. | Answer: 11.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+3 x+\frac{253}{4}>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{4}(x+11)(x-23)>0$, from which $-11<x<23$. On this interval, there are 22 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=22$. During this interval, $y$ takes integer values only for even $x$ - a total of 11 possibilities. Therefore, we get 11 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 11 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8$ (digits can repeat) so that the resulting 10-digit number is divisible by 18. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 3645.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 18, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 2 and by 9. To ensure divisibility by 2, we can choose the last digit from the available options as $0, 2, 4, 6$ or 8 (5 ways).
To ensure divisibility by nine, we proceed as follows. Choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9$ ways), and select the fourth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 9. Since these digits give all possible remainders when divided by $9 (0, 1, 2, \ldots, 8)$, and each remainder occurs exactly once, the last digit can be chosen in one way.
Applying the rule of product, we get that the total number of ways is $5 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 1 = 3645$. | 3645 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+9 x+19$. | Answer: 18.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+9 x+19>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{4}(x+2)(x-38)>0$, from which $-2<x<38$. On this interval, there are 37 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=37$. In this interval, $y$ takes integer values only for even $x$ - a total of 18 possibilities. Thus, we get 18 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 18 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8$ (digits can repeat) so that the resulting 10-digit number is divisible by 45. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 1458.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 45, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 5 and by 9. To ensure divisibility by 5, we can choose 0 or 5 as the last digit (2 ways).
To ensure divisibility by nine, we proceed as follows. We select three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9$ ways), and choose the fourth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 9. Since these digits give all possible remainders when divided by $9 (0,1,2, \ldots, 8)$, and each remainder occurs exactly once, the last digit can be chosen in one way.
Applying the rule of product, we get that there are $2 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 1=1458$ ways. | 1458 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+5 x+39$. | Answer: 12.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{4}+5 x+39>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{4}(x+6)(x-26)>0$, from which $-6<x<26$. On this interval, there are 25 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=25$. In this interval, $y$ takes integer values only for even $x$ - a total of 12 possibilities. Therefore, we get 12 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 12 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 * 2 *$, each of the 6 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9$ (digits can repeat) so that the resulting 12-digit number is divisible by 18. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 26244.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 18, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 2 and by 9. To ensure divisibility by 2, we can choose the last digit from the available options as $2, 4, 6$ or 8 (4 ways).
To ensure divisibility by nine, we proceed as follows. Choose four digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9$ ways), and select the fifth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 9. Since these digits give all possible remainders when divided by $9 (0,1,2, \ldots, 8)$, and each remainder occurs exactly once, the last digit can be chosen in one way.
Applying the rule of product, we get that the total number of ways is $4 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 9 \cdot 1=26244$. | 26244 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+13 x+42$. | Answer: 13.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+13 x+42>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{3}(x+3)(x-42)>0$, from which $-3<x<42$. On this interval, there are 41 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=41$. In this case, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 13 possibilities. Thus, we get 13 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 13 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Find the value of the expression $\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}$, where $a$ and $b$ are the largest and smallest roots of the equation $x^{3}-7 x^{2}+7 x=1$, respectively. | Answer: 34.
Solution. The given equation is equivalent to the following
$$
\left(x^{3}-1\right)-7\left(x^{2}-x\right)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}+x+1\right)-7 x(x-1)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}-6 x+1\right)=0,
$$
from which $x=1$ or $x=3 \pm \sqrt{8}$. The largest root is $a=3+\sqrt{8}$, and the smallest is $-b=3-\sqrt{8}$. Then
$$
\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}=\frac{3+\sqrt{8}}{3-\sqrt{8}}+\frac{3-\sqrt{8}}{3+\sqrt{8}}=\frac{(3+\sqrt{8})^{2}+(3-\sqrt{8})^{2}}{(3+\sqrt{8})(3-\sqrt{8})}=\frac{2(9+8)}{1}=34
$$ | 34 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2016 * * * * 02 * *$, each of the 6 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,5,7,9$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 12-digit number is divisible by 15. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 5184.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 15, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 5 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 5, we can choose 0 or 5 as the last digit from the available options (2 ways).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. Choose four digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and select the fifth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits, there are two digits divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 5), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get a total of $2 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=5184$ ways. | 5184 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+7 x+54$. | Answer: 8.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+7 x+54>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{3}(x+6)(x-27)>0$, from which $-6<x<27$. On this interval, there are 26 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=26$. In this interval, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 8 possibilities. Therefore, we get 8 points on the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 8 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Find the value of the expression $\frac{p}{q}+\frac{q}{p}$, where $p$ and $q$ are the largest and smallest roots of the equation $x^{3}+6 x^{2}+6 x=-1$, respectively. | Answer: 23.
Solution. The given equation is equivalent to the following
$$
\left(x^{3}+1\right)+6\left(x^{2}+x\right)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x+1)\left(x^{2}-x+1\right)+6 x(x+1)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x+1)\left(x^{2}+5 x+1\right)=0 \text {, }
$$
from which $x=-1$ or $x=\frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{21}}{2}$. The largest root is $p=\frac{-5+\sqrt{21}}{2}$, and the smallest is $-q=\frac{-5-\sqrt{21}}{2}$. Then
$$
\frac{p}{q}+\frac{q}{p}=\frac{-5+\sqrt{21}}{-5-\sqrt{21}}+\frac{-5-\sqrt{21}}{-5+\sqrt{21}}=\frac{(-5+\sqrt{21})^{2}+(-5-\sqrt{21})^{2}}{(-5-\sqrt{21})(-5+\sqrt{21})}=\frac{2(25+21)}{4}=23 .
$$ | 23 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2016 * * * * 02 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,6,7,8$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 11-digit number is divisible by 6. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 2160.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 6, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 2 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 2, we can choose the last digit from the available options as $0, 2, 4, 6, 8$ (5 ways).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. Choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and select the fourth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits there are two digits divisible by 3 (0 and 6), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 8), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get that in total $5 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2 = 2160$ ways. | 2160 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+5 x+72$. | Answer: 7.
Solution. Let's find those values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+5 x+72>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{3}(x+9)(x-24)>0$, from which $-9<x<24$. On this interval, there are 23 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=23$. During this time, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 7 possibilities. Therefore, we get 7 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 7 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Find the value of the expression $\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}$, where $a$ and $b$ are the largest and smallest roots of the equation $x^{3}-9 x^{2}+9 x=1$, respectively. | Answer: 62.
Solution. The given equation is equivalent to the following
$$
\left(x^{3}-1\right)-9\left(x^{2}-x\right)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}+x+1\right)-9 x(x-1)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}-8 x+1\right)=0
$$
from which $x=1$ or $x=4 \pm \sqrt{15}$. The largest root is $a=4+\sqrt{15}$, the smallest is $-b=4-\sqrt{15}$. Then
$$
\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}=\frac{4+\sqrt{15}}{4-\sqrt{15}}+\frac{4-\sqrt{15}}{4+\sqrt{15}}=\frac{(4+\sqrt{15})^{2}+(4-\sqrt{15})^{2}}{(4+\sqrt{15})(4-\sqrt{15})}=\frac{2(16+15)}{1}=62
$$ | 62 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2016 * * * * 02 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,5,7,9$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 11-digit number is divisible by 15. In how many ways can this be done? | # Answer: 864.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 15, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 5 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 5, we can choose 0 or 5 as the last digit from the available options (2 ways).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. We will choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and the fourth digit will be chosen so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits, there are two digits that are divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 5), this choice can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get that in total $2 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=864$ ways. | 864 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+20 x+63$. | Answer: 20.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+20 x+63>0 \Leftrightarrow-\frac{1}{3}(x+3)(x-63)>0$, from which $-3<x<63$. On this interval, there are 62 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=62$. In this case, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 20 possibilities. Thus, we get 20 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 20 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Find the value of the expression $\frac{p}{q}+\frac{q}{p}$, where $p$ and $q$ are the largest and smallest roots of the equation $x^{3}-8 x^{2}+8 x=1$, respectively. | # Answer: 47.
Solution. The given equation is equivalent to the following
$$
\left(x^{3}-1\right)-8\left(x^{2}-x\right)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}+x+1\right)-8 x(x-1)=0 \Leftrightarrow(x-1)\left(x^{2}-7 x+1\right)=0 \text {, }
$$
from which $x=1$ or $x=\frac{7 \pm \sqrt{45}}{2}$. The largest root is $p=\frac{7+\sqrt{45}}{2}$, and the smallest is $-q=\frac{7-\sqrt{45}}{2}$. Then
$$
\frac{p}{q}+\frac{q}{p}=\frac{7+\sqrt{45}}{7-\sqrt{45}}+\frac{7-\sqrt{45}}{7+\sqrt{45}}=\frac{(7+\sqrt{45})^{2}+(7-\sqrt{45})^{2}}{(7+\sqrt{45})(7-\sqrt{45})}=\frac{2(49+45)}{4}=47
$$ | 47 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2016 * * * * 02 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,7,8,9$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 11-digit number is divisible by 6. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 1728.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 6, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 2 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 2, we can choose the last digit from the available options as $0, 2, 4, 8$ (4 ways).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. Choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and select the fourth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits there are two digits that are divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 8), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get that in total $4 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=1728$ ways. | 1728 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{9}+50$. | Answer: 7.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{9}+50>0 \Leftrightarrow x^{2}<450$, from which $-\sqrt{450}<x<\sqrt{450}$. On this interval, there are 21 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=21$. During this time, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 7 possibilities. Therefore, we get 7 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 7 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 * 2 *$, each of the 6 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,5,7,9$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 12-digit number is divisible by 75. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 2592.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 75, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 25 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 25, we can choose 5 as the last digit from the available options (1 way).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. Select four digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and choose the fifth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits, there are two digits divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 5), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get a total of $1 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=2592$ ways. | 2592 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. Plot on the plane $(x ; y)$ the set of points satisfying the equation $|15 x|+|8 y|+|120-15 x-8 y|=120$, and find the area of the resulting figure. | Answer: 60.
Solution. Note that the equality $|a|+|b|+|c|=a+b+c$ holds if and only if the numbers $a, b$, and $c$ are non-negative (since if at least one of them is negative, the left side is greater than the right). Therefore, the first equation is equivalent to the system of inequalities
$$
\left\{\begin{array} { l }
{ 1 5 x \geq 0 , } \\
{ 8 y \geq 0 , } \\
{ 1 2 0 - 1 5 x - 8 y \geq 0 }
\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x \geq 0 \\
y \geq 0 \\
15 x+8 y \leq 120
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
This system defines a triangle on the plane with vertices $E(8 ; 0), G(0 ; 15), N(0 ; 0)$, the area of which is equal to 60. | 60 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane that have natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lie on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+70$. | Answer: 4.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+70>0 \Leftrightarrow x^{2}<210$, from which $-\sqrt{210}<x<\sqrt{210}$. On this interval, there are 14 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=14$. During this time, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 4 possibilities. Therefore, we get 7 points belonging to the parabola, both of whose coordinates are natural numbers. | 4 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 02 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,7,8,9$ (digits can repeat) so that the resulting 11-digit number is divisible by 12. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 1296.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 12, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 4 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 4, we can choose 0, 4, or 8 as the last digit (3 ways).
To ensure divisibility by 3, we proceed as follows. We will choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and select the fourth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits there are two digits divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 8), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get that in total $3 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=1296$ ways. | 1296 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. On the plane $(x ; y)$, plot the set of points satisfying the equation $|3 x|+|4 y|+|48-3 x-4 y|=48$, and find the area of the resulting figure. | Answer: 96.
Solution. Note that the equality $|a|+|b|+|c|=a+b+c$ holds if and only if the numbers $a, b$, and $c$ are non-negative (since if at least one of them is negative, the left side is greater than the right). Therefore, the first equation is equivalent to the system of inequalities
$$
\left\{\begin{array} { l }
{ 3 x \geq 0 , } \\
{ 4 y \geq 0 , } \\
{ 4 8 - 3 x - 4 y \geq 0 }
\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x \geq 0 \\
y \geq 0 \\
3 x+4 y \leq 48
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
This system defines a triangle on the plane with vertices $E(16 ; 0), G(0 ; 12), N(0 ; 0)$, the area of which is equal to 96. | 96 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the $x O y$ plane having natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lying on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{9}+33$. | Answer: 5.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{9}+33>0 \Leftrightarrow x^{2}<297$, from which $-\sqrt{297}<x<\sqrt{297}$. On this interval, there are 17 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=17$. At the same time, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 5 possibilities. Thus, we get 5 points belonging to the parabola, both coordinates of which are natural numbers. | 5 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 07 *$, each of the 5 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,5,6,7$ (digits can repeat) so that the resulting 11-digit number is divisible by 75. In how many ways can this be done? | # Answer: 432.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 75, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 25 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 25, we can choose 5 as the last digit (1 way) from the available options.
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. We will choose three digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and the fifth digit will be chosen so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits, there are two digits divisible by 3 (0 and 6), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 5), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get that in total $1 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=432$ ways. | 432 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. Plot on the plane $(x ; y)$ the set of points satisfying the equation $|5 x|+|12 y|+|60-5 x-12 y|=60$, and find the area of the resulting figure. | Answer: 30.
Solution. Note that the equality $|a|+|b|+|c|=a+b+c$ holds if and only if the numbers $a, b$, and $c$ are non-negative (since if at least one of them is negative, the left side is greater than the right). Therefore, the first equation is equivalent to the system of inequalities
$$
\left\{\begin{array} { l }
{ 5 x \geq 0 } \\
{ 1 2 y \geq 0 , } \\
{ 6 0 - 5 x - 1 2 y \geq 0 }
\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x \geq 0 \\
y \geq 0 \\
5 x+12 y \leq 60
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
This system defines a triangle on the plane with vertices $E(12 ; 0), G(0 ; 5), N(0 ; 0)$, the area of which is 30. | 30 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
1. Find the number of points in the plane $x O y$ that have natural coordinates $(x, y)$ and lie on the parabola $y=-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+98$ | Answer: 5.
Solution. Let's find the values of $x$ for which $y$ is positive: $-\frac{x^{2}}{3}+98>0 \Leftrightarrow x^{2}<294$, from which $-\sqrt{294}<x<\sqrt{294}$. On this interval, there are 17 natural values of $x: x=1, x=2, \ldots, x=17$. At the same time, $y$ takes integer values only when $x$ is divisible by 3 - a total of 5 possibilities. Thus, we get 5 points belonging to the parabola, both coordinates of which are natural numbers. | 5 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. In the number $2 * 0 * 1 * 6 * 0 * 2 *$, each of the 6 asterisks needs to be replaced with any of the digits $0,2,4,5,7,9$ (digits can be repeated) so that the resulting 12-digit number is divisible by 12. In how many ways can this be done? | Answer: 5184.
Solution. For a number to be divisible by 12, it is necessary and sufficient that it is divisible by 4 and by 3. To ensure divisibility by 4, we can choose 0 or 4 as the last digit from the available options (2 ways).
To ensure divisibility by three, we proceed as follows. We will choose four digits arbitrarily (this can be done in $6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6$ ways), and then select the fifth digit so that the sum of all the digits of the number is divisible by 3. Since among the given digits there are two digits that are divisible by 3 (0 and 9), two digits that give a remainder of 1 when divided by 3 (4 and 7), and two digits that give a remainder of 2 when divided by 3 (2 and 5), this selection can be made in two ways.
Applying the rule of product, we get a total of $2 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 6 \cdot 2=5184$ ways. | 5184 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
4. On the plane $(x ; y)$, plot the set of points satisfying the equation $|4 x|+|3 y|+|24-4 x-3 y|=24$, and find the area of the resulting figure.
# | # Answer: 24.
Solution. Note that the equality $|a|+|b|+|c|=a+b+c$ holds if and only if the numbers $a, b$, and $c$ are non-negative (since if at least one of them is negative, the left side is greater than the right). Therefore, the first equation is equivalent to the system of inequalities
$$
\left\{\begin{array} { l }
{ 4 x \geq 0 , } \\
{ 3 y \geq 0 , } \\
{ 2 4 - 4 x - 3 y \geq 0 }
\end{array} \Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x \geq 0 \\
y \geq 0 \\
4 x+3 y \leq 24
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
This system defines a triangle on the plane with vertices $E(6 ; 0), G(0 ; 8), N(0 ; 0)$, the area of which is 24. | 24 | Geometry | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Given a regular 20-gon $M$. Find the number of quadruples of vertices of this 20-gon that are the vertices of convex quadrilaterals, which have at least one pair of parallel sides. | Answer: 765.
Solution. Let's inscribe the given polygon $K_{1} K_{2} \ldots K_{20}$ in a circle. Each quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is determined by a pair of parallel chords with endpoints at points $K_{1}, \ldots, K_{20}$.
Consider a chord connecting two adjacent vertices of the polygon, for example, $K_{6} K_{7}$. There are 9 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{8}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 10 parallel chords. From these, we can form $C_{10}^{2}=45$ pairs of parallel segments.
We will get similar sets if we consider all chords parallel to $K_{1} K_{2}, \ldots, K_{10} K_{11}$, a total of 10 such sets.
Now, let's take a chord connecting vertices that are one apart from each other, for example, $K_{6} K_{8}$. There are 8 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{9}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 9 parallel chords. From these, we can form $C_{9}^{2}=36$ pairs of parallel segments. There are also 10 such sets.
In total, we get $10 \cdot 45 + 10 \cdot 36 = 810$ quadrilaterals. With this method of counting, rectangles have been counted twice. Note that both diagonals of an inscribed rectangle in a circle are diameters, and there are 10 diameters with vertices at the given points, thus we get $C_{10}^{2}=45$ rectangles. Therefore, we have $810 - 45 = 765$ quadrilaterals with at least one pair of parallel sides. | 765 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. Find the number of natural numbers $k$, not exceeding 291000, such that $k^{2}-1$ is divisible by 291. | Answer: 4000.
Solution. By factoring the dividend and divisor, we get the condition $(k-1)(k+1):(3 \cdot 97)$. This means that one of the numbers $(k+1)$ or $(k-1)$ is divisible by 97. Let's consider two cases.
a) $(k+1): 97$, i.e., $k=97 p+96, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $(97 p+95)(97 p+97):(3 \cdot 97) \Leftrightarrow(97 p+95)(p+1): 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q+1, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=3 q+2, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=291 q+193, k=291 q+290, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
b) $(k-1): 97$, i.e., $k=97 p+1, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $97 p(97 p+2):(3 \cdot 97) \Leftrightarrow(97 p+2) p ; 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q+1, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=3 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=291 q+98$, $k=291 q+1, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
Thus, the numbers that satisfy the condition of the problem are those that give remainders of $193, 290, 98, 1$ when divided by 291, meaning that every 4 out of 291 consecutive numbers fit. Since $291000=291 \cdot 1000$, we get $4 \cdot 1000=4000$ numbers. | 4000 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Given a regular 16-gon $M$. Find the number of quadruples of vertices of this 16-gon that are the vertices of convex quadrilaterals, which have at least one pair of parallel sides. | Answer: 364.
Solution. Let's inscribe the given polygon $K_{1} K_{2} \ldots K_{16}$ in a circle. Each quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is determined by a pair of parallel chords with endpoints at points $K_{1}, \ldots, K_{16}$.
Consider a chord connecting two adjacent vertices of the polygon, for example, $K_{6} K_{7}$. There are 7 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{8}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 8 parallel chords. From these, we can form $C_{8}^{2}=28$ pairs of parallel segments.
We will get similar sets if we consider all chords parallel to $K_{1} K_{2}, \ldots, K_{8} K_{9}$ - a total of 8 such sets.
Now, let's take a chord connecting vertices that are one apart, for example, $K_{6} K_{8}$. There are 6 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{9}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 7 parallel chords. From these, we can form $C_{7}^{2}=21$ pairs of parallel segments. There are also 8 such sets.
In the end, we get $8 \cdot 28 + 8 \cdot 21 = 392$ quadrilaterals. With this method of counting, rectangles were counted twice. Note that both diagonals of an inscribed rectangle in a circle are diameters, and there are 8 diameters with vertices at the given points, thus we get $C_{8}^{2}=28$ rectangles. Therefore, we have $392 - 28 = 364$ quadrilaterals with at least one pair of parallel sides. | 364 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. Find the number of natural numbers $k$, not exceeding 445000, such that $k^{2}-1$ is divisible by 445. Answer: 4000. | Solution. Factoring the dividend and divisor, we get the condition $(k-1)(k+1):(5 \cdot 89)$. This means that one of the numbers $(k+1)$ or $(k-1)$ is divisible by 89. Let's consider two cases.
a) $(k+1): 89$, i.e., $k=89 p+88, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $(89 p+87)(89 p+89):(5 \cdot 89) \Leftrightarrow(89 p+87)(p+1): 5$. The first factor is divisible by 5 when $p=5 q+2, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=5 q+4, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=445 q+276, k=445 q+444, q \in Z$.
b) $(k-1): 89$, i.e., $k=89 p+1, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $89 p(89 p+2):(5 \cdot 89) \Leftrightarrow(89 p+2) p: 5$. The first factor is divisible by 5 when $p=5 q+2, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=5 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=445 q+179$, $k=445 q+1, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
Thus, the numbers that satisfy the condition of the problem are those that give remainders $276, 444, 179, 1$ when divided by 445, meaning that every 4 out of 445 consecutive numbers fit. Since $445000=445 \cdot 1000$, we get $4 \cdot 1000=4000$ numbers. | 4000 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Given a regular 22-gon $M$. Find the number of quadruples of vertices of this 22-gon that are the vertices of convex quadrilaterals, which have at least one pair of parallel sides. | Answer: 1045.
Solution. Let's inscribe the given polygon $K_{1} K_{2} \ldots K_{22}$ in a circle. Each quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is determined by a pair of parallel chords with endpoints at points $K_{1}, \ldots, K_{22}$.
Consider a chord connecting two adjacent vertices of the polygon, for example, $K_{6} K_{7}$. There are 10 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{8}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 11 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{11}^{2}=55$ pairs of parallel segments.
We will get similar sets if we consider all chords parallel to $K_{1} K_{2}, \ldots, K_{11} K_{12}$ - a total of 11 such sets.
Now, let's take a chord connecting vertices that are one apart from each other, for example, $K_{6} K_{8}$. There are 9 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{9}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 10 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{10}^{2}=45$ pairs of parallel segments. There are also 11 such sets.
In the end, we get $11 \cdot 55 + 11 \cdot 45 = 1100$ quadrilaterals. With this method of counting, rectangles were counted twice. Note that both diagonals of an inscribed rectangle in a circle are diameters, and there are 11 diameters with vertices at the given points, thus we get $C_{11}^{2}=55$ rectangles. Therefore, we have $1100 - 55 = 1045$ quadrilaterals with at least one pair of parallel sides. | 1045 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. Find the number of natural numbers $k$, not exceeding 485000, such that $k^{2}-1$ is divisible by 485. | Answer: 4000.
Solution. By factoring the dividend and divisor, we get the condition $(k-1)(k+1):(5 \cdot 97)$. This means that one of the numbers $(k+1)$ or $(k-1)$ is divisible by 97. Let's consider two cases.
a) $(k+1): 97$, i.e., $k=97 p+96, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $(97 p+95)(97 p+97):(5 \cdot 97) \Leftrightarrow(97 p+95)(p+1): 5$. The first factor is divisible by 5 when $p=5 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=5 q+4, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=485 q+96, k=485 q+484, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
b) $(k-1): 97$, i.e., $k=97 p+1, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $97 p(97 p+2):(5 \cdot 97) \Leftrightarrow(97 p+2) p: 5$. The first factor is divisible by 5 when $p=5 q+4, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=5 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=485 q+389$, $k=485 q+1, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
Thus, the numbers that satisfy the condition of the problem are those that give remainders $96,484,389,1$ when divided by 485, meaning that every 4 out of 485 consecutive numbers fit. Since $485000=485 \cdot 1000$, we get $4 \cdot 1000=4000$ numbers. | 4000 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Given a regular 18-gon $M$. Find the number of quadruples of vertices of this 18-gon that are the vertices of convex quadrilaterals, which have at least one pair of parallel sides. | Answer: 540.
Solution. Let's inscribe the given polygon $K_{1} K_{2} \ldots K_{18}$ in a circle. Each quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is determined by a pair of parallel chords with endpoints at points $K_{1}, \ldots, K_{18}$.
Consider a chord connecting two adjacent vertices of the polygon, for example, $K_{6} K_{7}$. There are 8 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{8}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 9 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{9}^{2}=36$ pairs of parallel segments.
We will get similar sets if we consider all chords parallel to $K_{1} K_{2}, \ldots, K_{9} K_{10}$ - a total of 9 such sets.
Now, let's take a chord connecting vertices that are one apart from each other, for example, $K_{6} K_{8}$. There are 7 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{9}$, etc.), i.e., we get a set of 8 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{8}^{2}=28$ pairs of parallel segments. There are also 9 such sets.
In the end, we get $9 \cdot 36 + 9 \cdot 28 = 576$ quadrilaterals. With this method of counting, rectangles were counted twice. Note that both diagonals of an inscribed rectangle in a circle are diameters, and there are 8 diameters with vertices at the given points, thus we get $C_{9}^{2}=36$ rectangles. Therefore, we have $576 - 36 = 540$ quadrilaterals with at least one pair of parallel sides. | 540 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
3. Find the number of natural numbers $k$, not exceeding 267000, such that $k^{2}-1$ is divisible by 267. | Answer: 4000.
Solution. By factoring the dividend and divisor, we get the condition $(k-1)(k+1):(3 \cdot 89)$. This means that one of the numbers $(k+1)$ or $(k-1)$ is divisible by 89. Let's consider two cases.
a) $(k+1): 89$, i.e., $k=89 p+88, p \in \mathbb{Z}$. Then we get $(89 p+87)(89 p+89):(3 \cdot 89) \Leftrightarrow (89 p+87)(p+1): 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q, q \in \mathbb{Z}$, and the second factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q+2, q \in \mathbb{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=267 q+88, k=267 q+266, q \in \mathbb{Z}$.
b) $(k-1): 89$, i.e., $k=89 p+1, p \in \mathbb{Z}$. Then we get $89 p(89 p+2):(3 \cdot 89) \Leftrightarrow (89 p+2) p \vdots 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q+2, q \in \mathbb{Z}$, and the second factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q, q \in \mathbb{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=267 q+179$, $k=267 q+1, q \in \mathbb{Z}$.
Thus, the numbers that satisfy the condition of the problem are those that give remainders $88, 266, 179, 1$ when divided by 267, meaning that every 4 out of 267 consecutive numbers fit. Since $267000=267 \cdot 1000$, we get $4 \cdot 1000=4000$ numbers. | 4000 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. Find the number of pairs of integers $(x ; y)$ that satisfy the condition $5 x^{2}-6 x y+y^{2}=6^{100}$. | Answer: 19594.
Solution: By factoring the left and right sides of the equation, we get $(5 x-y)(x-y)=2^{100} \cdot 3^{100}$. Since each factor on the left side is an integer, it follows that
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
5 x - y = 2 ^ { k } \cdot 3 ^ { l }, \\
x - y = 2 ^ { 1 0 0 - k } \cdot 3 ^ { 1 0 0 - l }
\end{array} \text { or } \left\{\begin{array}{l}
5 x-y=-2^{k} \cdot 3^{l}, \\
x-y=-2^{100-k} \cdot 3^{100-l}
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
where $k$ and $l$ are integers from the interval $[0 ; 100]$.
Let's find the number of solutions to the first system. Expressing $x$ and $y$ from it, we get
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x=2^{k-2} \cdot 3^{l}-2^{98-k} \cdot 3^{100-l} \\
y=2^{k-2} \cdot 3^{l}-5 \cdot 2^{98-k} \cdot 3^{100-l}
\end{array}\right.
$$
Consider the first equation. The exponents in the powers of three are non-negative. The sum of the exponents in the powers of two is 96, so at least one of them is positive, i.e., the corresponding term is an integer. Since the left side of the equation is also an integer, the second term on the right side of the equation must also be an integer. Therefore, for the existence of integer solutions, it is necessary and sufficient that $2 \leq k \leq 98,0 \leq l \leq 100-$ a total of $97 \cdot 101=9797$ options.
The second system also has 9797 solutions; thus, there are 19594 solutions in total. | 19594 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. Find the number of pairs of integers $(x ; y)$ that satisfy the condition $6 x^{2}-7 x y+y^{2}=10^{100}$. | Answer: 19998.
Solution: By factoring the left and right sides of the equation, we get $(6 x-y)(x-y)=2^{100} \cdot 5^{100}$. Since each factor on the left side is an integer, it follows that
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
6 x - y = 2 ^ { k } \cdot 5 ^ { l } , \\
x - y = 2 ^ { 1 0 0 - k } \cdot 5 ^ { 1 0 0 - l }
\end{array} \text { or } \left\{\begin{array}{l}
6 x-y=-2^{k} \cdot 5^{l} \\
x-y=-2^{100-k} \cdot 5^{100-l}
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
where $k$ and $l$ are integers from the interval $[0 ; 100]$.
Let's find the number of solutions to the first system. Expressing $x$ and $y$ from it, we get
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x=2^{k} \cdot 5^{l-1}-2^{100-k} \cdot 5^{99-l} \\
y=2^{k} \cdot 5^{l-1}-6 \cdot 2^{100-k} \cdot 5^{99-l}
\end{array}\right.
$$
Consider the first equation. The exponents of the powers of two are non-negative. The sum of the exponents of the powers of five is 98, so at least one of them is positive, i.e., the corresponding term is an integer. Since the left side of the equation is also an integer, the second term on the right side of the equation must also be an integer. Therefore, for the existence of integer solutions, it is necessary and sufficient that $0 \leq k \leq 100,1 \leq l \leq 99$ - a total of $99 \cdot 101=9999$ options.
The second system also has 9999 solutions; thus, there are 19998 solutions in total. | 19998 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. Find the number of pairs of integers $(x ; y)$ that satisfy the condition $x^{2}+6 x y+5 y^{2}=10^{100}$. | Answer: 19594.
Solution: By factoring the left and right sides of the equation, we get $(x+5 y)(x+y)=2^{100} \cdot 5^{100}$. Since each factor on the left side is an integer, it follows that
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x+5 y=2^{k} \cdot 5^{l}, \\
x+y=2^{100-k} \cdot 5^{100-l}
\end{array} \text { or } \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x+5 y=-2^{k} \cdot 5^{l}, \\
x+y=-2^{100-k} \cdot 5^{100-l}
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
where $k$ and $l$ are integers from the interval $[0 ; 100]$.
Let's find the number of solutions to the first system. Expressing $x$ and $y$ from it, we get
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
y=2^{k-2} \cdot 5^{l}-2^{98-k} \cdot 5^{100-l} \\
x=5 \cdot 2^{98-k} \cdot 5^{100-l}-2^{k-2} \cdot 5^{l}
\end{array}\right.
$$
Consider the first equation. The exponents of the powers of five are non-negative. The sum of the exponents of the powers of two is 96, so at least one of them is positive, i.e., the corresponding term is an integer. Since the left side of the equation is also an integer, the second term on the right side of the equation must also be an integer. Therefore, for the existence of integer solutions, it is necessary and sufficient that $2 \leq k \leq 98,0 \leq l \leq 100-$ a total of $97 \cdot 101=9797$ options.
The second system also has 9797 solutions; thus, there are 19594 solutions in total. | 19594 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. Find the number of pairs of integers $(x ; y)$ that satisfy the condition $x^{2}+7 x y+6 y^{2}=15^{50}$. | Answer: 4998.
Solution: Factoring the left and right sides of the equation, we get $(x+6 y)(x+y)=5^{50} \cdot 3^{50}$. Since each factor on the left side is an integer, it follows that
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x+6 y=5^{k} \cdot 3^{l}, \\
x+y=5^{50-k} \cdot 3^{50-l}
\end{array} \text { or } \left\{\begin{array}{l}
x+6 y=-5^{k} \cdot 3^{l}, \\
x+y=-5^{50-k} \cdot 3^{50-l}
\end{array}\right.\right.
$$
where $k$ and $l$ are integers from the interval $[0 ; 50]$.
Let's find the number of solutions to the first system. Expressing $x$ and $y$ from it, we get
$$
\left\{\begin{array}{l}
x=6 \cdot 5^{49-k} \cdot 3^{50-l}-5^{k-1} \cdot 3^{l} \\
y=5^{k-1} \cdot 3^{l}-5^{49-k} \cdot 3^{50-l}
\end{array}\right.
$$
Consider the first equation. The exponents in the powers of three are non-negative. The sum of the exponents in the powers of five is 48, so at least one of them is positive, i.e., the corresponding term is an integer. Since the left side of the equation is also an integer, the second term on the right side of the equation must also be an integer. Therefore, for the existence of integer solutions, it is necessary and sufficient that $1 \leq k \leq 49, 0 \leq l \leq 50$ - a total of $49 \cdot 51=2499$ options.
"Phystech-2015", 10th grade, solutions to ticket 8
The second system also has 2499 solutions; thus, there are 4998 solutions in total. | 4998 | Algebra | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
2. Find the number of natural numbers $k$, not exceeding 242400, such that $k^{2}+2 k$ is divisible by 303. Answer: 3200. | Solution. Factoring the dividend and divisor, we get the condition $k(k+2):(3 \cdot 101)$. This means that one of the numbers $k$ or $(k+2)$ is divisible by 101. Let's consider two cases.
a) $k: 101$, i.e., $k=101 p, p \in \mathrm{Z}$. Then we get $101 p(101 p+2):(3 \cdot 101) \Leftrightarrow p(101 p+2): 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=3 q+2, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=303 q, k=303 q+202, q \in \mathrm{Z}$.
b) $(k+2): 101$, i.e., $k=101 p+99, p \in Z$. Then we get $(101 p+99)(101 p+101):(3 \cdot 101) \Leftrightarrow(101 p+99)(p+1): 3$. The first factor is divisible by 3 when $p=3 q, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, and the second when $p=3 q+2, q \in \mathrm{Z}$, from which we obtain that $k=303 q+99, k=303 q+301, q \in Z$.
Thus, the numbers that satisfy the condition of the problem are those that give remainders $0, 202, 99, 301$ when divided by 303, meaning that every 4 out of 303 consecutive numbers fit. Since $242400=303 \cdot 800$, we get $4 \cdot 800=3200$ numbers. | 3200 | Number Theory | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
5. Given a regular 20-gon $M$. Find the number of quadruples of vertices of this 20-gon that are the vertices of trapezoids. | Answer: 720.
Solution. Let's inscribe the given polygon $K_{1} K_{2} \ldots K_{20}$ in a circle. Each trapezoid is defined by a pair of parallel chords with endpoints at points $K_{1}, \ldots, K_{20}$.
Consider a chord connecting two adjacent vertices of the polygon, for example, $K_{6} K_{7}$. There are 9 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{8}$ and so on), i.e., we get a set of 10 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{10}^{2}=45$ pairs of parallel segments.
We will get similar sets if we consider all chords parallel to $K_{1} K_{2}, \ldots, K_{10} K_{11}$, a total of 10 such sets.
Now, let's take a chord connecting vertices that are one apart from each other, for example, $K_{6} K_{8}$. There are 8 more chords parallel to it ( $K_{5} K_{9}$ and so on), i.e., we get a set of 9 chords parallel to each other. From these, we can form $C_{9}^{2}=36$ pairs of parallel segments. There are also 10 such sets.
In total, we get $10 \cdot 45 + 10 \cdot 36 = 810$ quadrilaterals. With this method of counting, rectangles have been counted twice. Note that both diagonals of an inscribed rectangle are diameters, and there are 10 diameters with vertices at the given points, thus we have $C_{10}^{2}=45$ rectangles. Subtracting twice the number of rectangles, we get $810 - 90 = 720$ quadrilaterals that have at least one pair of parallel sides. | 720 | Combinatorics | math-word-problem | Yes | Yes | olympiads | false |
Subsets and Splits